
Table of contents:
- Author Bailey Albertson albertson@usefultipsdiy.com.
- Public 2024-01-17 22:26.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 07:32.
Renal failure in cats: early diagnosis - long life

Renal failure can lie in wait for a cat and its owner as a complication of any disease, developing acutely, or secretly pursuing a pet for years, manifesting itself only in its advanced stage. If the owner of the cat pays attention to the pet and its health, he is able to save his pet even from such a serious illness.
Content
-
1 Renal failure and its causes
-
1.1 Acute renal failure
1.1.1 Video: Acute Renal Failure in Cats
- 1.2 Chronic renal failure
- 1.3 Factors contributing to the development of the disease
-
-
2 How does renal failure manifest in cats?
- 2.1 Signs of an acute form
-
2.2 Symptoms of the chronic form
2.2.1 Video: symptoms of renal failure
-
3 Diagnosis of renal failure in cats
3.1 Video: Diagnosing Renal Failure in Cats
-
4 When you need to urgently contact your veterinarian
4.1 Inpatient treatment
-
5 Home treatment
-
5.1 Use of medications
- 5.1.1 Table: Overview of drugs used to treat kidney failure
- 5.1.2 Photo Gallery: Medicines for the Treatment of Renal Failure in Cats
- 5.2 The use of folk remedies
- 5.3 Diet
- 5.4 Video: Treatment of Chronic Renal Failure in Animals
- 5.5 Care rules
- 5.6 Features of the treatment of pregnant cats and kittens
-
- 6 Prevention of renal failure
- 7 Veterinarian recommendations
Renal failure and its causes
With the formation of renal failure, the kidneys lose the ability to maintain the constancy of the internal environment of the body due to the regulation of the exchange of water and salts, as well as the elimination of toxic compounds, both formed in the body itself and entering it from the outside, which causes intoxication.
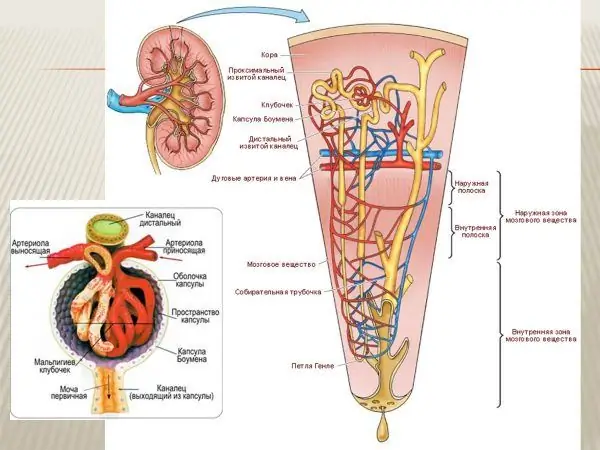
In renal failure, the nephrons - structural units of the kidneys
Acute renal failure
Acute renal failure is an urgent life-threatening condition, expressed in a rapid and pronounced decrease in renal function. Its development occurs rapidly and is manifested by gross violations of the water-salt, acid-base balance, as well as azotemia (an increased content of nitrogenous metabolic products in the blood, normally excreted by the kidneys). Acute renal failure can be reversible as a result of proper treatment.
Based on the causative factors, forms of acute renal failure are distinguished:
-
Prerenal - it is also called "prerenal", the damaging factor affects outside the excretory system and causes a sharp drop in total blood pressure, as a result of which it becomes impossible to filter blood in the nephrons and the formation of urine. The most common reasons are:
-
shocks of various origins:
- hemorrhagic;
- toxic;
- heatstroke;
- dehydration (dehydration);
- insufficiency of heart function.
-
-
Renal - when the damaging factor acts directly on the kidney tissue:
- kidney abscess;
- acute glomerulonephritis - inflammation of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys;
- acute interstitial nephritis - when the inflammatory process affects the renal tubules and the interstitial tissue located between them;
- severe infectious diseases, for example, viral immunodeficiency;
-
poisoning:
- ethylene glycol;
- heavy metal salts;
- medicines;
-
plants, especially lilies;

Lily flowers Eating a lily causes acute kidney failure in cats
-
hemolytic conditions - in which, as a result of massive hemolysis (destruction) of erythrocytes in the bloodstream, their debris clog the renal glomeruli and tubules:
- hemobartonellosis;
- hemolysis-causing poisons - vinegar essence, snake venoms;
- severe septic conditions;
- complication of blood transfusion.
-
Postrenal - This is usually a blockage of the urinary tract caused by:
- stones with urolithiasis;
- compression or growth of a tumor.
Video: Acute Renal Failure in Cats
Chronic renal failure
In chronic renal failure, kidney function decreases slowly but steadily, while nephrons - structural units of the kidneys - are replaced by fibrosis (proliferation of connective tissue). Symptoms develop slowly, since the preserved nephrons are able to compensate for the function of the lost ones for a long time, and the main symptoms appear when more than 75% of the units stop working.
The most common reasons:
-
chronic kidney disease:
- chronic forms of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis;
- amyloid dystrophy of the kidneys - when an abnormal protein - amyloid is deposited in the cells of the kidneys;
- urolithiasis disease;
-
common diseases:
- diabetes;
- uric acid diathesis;
- malformations of the kidneys - polycystic, while the renal tissue contains cysts - hollow liquid formations, the size of which increases, which causes the death of functioning nephrons, with the help of treatment it is possible only to temporarily suspend the irreversible process (the pathology is characteristic of Persian, British cats, their mestizos);
-
chronic intoxication:
- heavy metals;
- antibacterial drugs.
Stages of chronic renal failure:
- Non-azotemic - creatinine <140 μmol / L.
- Initial renal azotemia - creatinine 140-250 µmol / L.
- Moderate renal azotemia - creatinine 250-440 μmol / l.
- Severe renal azotemia - creatinine> 440 μmol / L.
The forecast depends on:
- the current stage of kidney failure;
- the achieved effect of the treatment;
- the pet's initial health.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease
Risk factors for the development of the disease include:
-
increased risk factors:
- existing kidney pathology;
- extensive traumatic injuries;
-
severe general diseases:
- liver pathology;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- sepsis;
- heredity;
-
additional risk factors:
- dehydration (dehydration);
- feverish conditions;
- long-term hypertension or hypotension;
- electrolyte disturbances;
- elderly age.
How does renal failure manifest in cats?
Symptoms of kidney failure in cats depend on the form. The clinical manifestations of acute and chronic forms of renal failure differ.
Signs of an acute form
The acute form of renal failure is manifested by:
- apathy;
- a decrease in the amount of separated urine up to its complete absence - anuria;
- swelling;
- palpitations;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea, often of a watery nature, sometimes with an admixture of blood;
- the smell of acetone or urine from the mouth;
- lack of appetite;
- decrease in body temperature;
- soreness in the kidney area, an increase in their size (determined by palpation).
Chronic symptoms
In the chronic form, symptoms appear gradually and are much milder than in acute renal failure:
- increased amount of urine and thirst;
-
a decrease in skin turgor, the skin fold does not straighten out for a long time;

Cat's withers If you collect the skin on the withers of the cat in a fold and release, but it does not immediately take its previous shape - the animal is dehydrated
- tarnishing of the coat (looks disheveled and unkempt);
- gradual weight loss until exhaustion;
- increased blood pressure, possible pulmonary edema, thrombosis, arrhythmias;
- an increase in the level of intracranial and intraocular pressure, the development of blindness is possible;
- development of ulcerative stomatitis;
- smell of ammonia from the mouth;
- constipation, occasionally followed by diarrhea;
- purulent processes with localization in the oral and nasal cavities - odontogenic abscesses, sinusitis;
- in the later stages - refusal of food and water;
- general depression, followed by short-term periods of excitement - as a manifestation of toxic encephalopathy caused by exposure of the brain to products of impaired protein metabolism;
- convulsions;
-
coma.

A thin cat lies on the table In chronic renal failure, the first to notice are the thinness of the animal and the hair tousled from dehydration.
Video: symptoms of kidney failure
Diagnosing kidney failure in cats
Diagnosis of renal failure in cats is based on:
-
collecting an anamnesis of the disease based on questioning the owner of the sick pet, special attention is paid to:
- collection of information about existing diseases;
- heredity;
- cat nutrition;
- the possibility of contact with medicines, toxic substances and plants;
- examination data of the animal (signs characteristic of an acute or chronic form are found);
-
laboratory research data, which play a leading role:
-
biochemical blood test shows:
-
increase:
- products of nitrogen metabolism (urea, creatinine, nitrogen);
- ions of potassium, magnesium, phosphorus;
- amylase;
- lowering calcium levels;
- the formation of acidosis (increased acidity);
-
-
general urine analysis:
- in the acute form, protein and cylinders consisting of it, erythrocytes, dead renal epithelium, glucose appear in the urine;
- in the chronic form, both the density and the specific gravity of urine are very low, therefore, the protein is almost undetectable; the cellular composition is also scarce due to the high dilution of urine and is represented by dystrophic cells of the tubular epithelium and casts; the urine reaction is very acidic;
- when bacterial complications appear, urine alkalizes, neutrophils and bacterial flora are determined in it, and the level of protein rises;
-
general blood analysis:
- in the acute form, it has no characteristic features;
-
in chronic form, pays attention:
- severe anemia, since it is the kidneys that produce erythropoietin, a hormone that regulates the formation of red blood cells;
- an increase in the content of neutrophils;
- increased ESR.
-
-
Ultrasound of the kidneys: changes in the structure of the kidneys caused by their disease or malformation during development are revealed; the presence of stones and tumors; in the acute form, the size of the kidneys is enlarged, their tissue is edematous; in the chronic form, the size of the kidneys is less than normal, the outline is clear and uneven - these are “shriveled” kidneys;

Cat ultrasound Ultrasound of the kidneys allows you to visualize changes in their structure and size
- X-ray research methods - are usually carried out with contrast and allow you to assess the change in the anatomical structure of the kidneys, the presence of stones, ureteral patency, as well as the glomerular filtration rate;
- computed tomography, including with contrasting - gives the clearest idea of the violation in the structure of the kidneys, unfortunately, in few places veterinary tomographs are installed; The disadvantage is also the high cost of the examination, which does not yet allow it to be carried out in large quantities for all animals in need.
Video: diagnosis of renal failure in cats
When you urgently need to contact the veterinarian
The veterinarian should be contacted as soon as the first signs of kidney failure in the cat appear. Attention should be paid to the reduction or absence of urine discharge against the background of a general deterioration in the cat's condition. In the chronic form, the first symptoms are usually increased thirst and increased volume of urine, but it can also be vomiting, diarrhea, and lack of appetite. If the past of the cat is unknown, then upon examination, the acute form will differ from the chronic one by the absence of strong thirst, exhaustion, as well as a reduced volume of urine or anuria - its complete absence.
Inpatient treatment
The acute form of kidney failure is life threatening, so its treatment is carried out in a hospital equipped with intensive care, and can take up to 10-14 days. In a clinic, the cat receives emergency assistance:
- the cause of acute renal failure is eliminated, for example, a calculus that blocked the outflow of urine, urine is excreted by a catheter;
- treatment of the underlying pathology, complicated by failure of renal function, is performed;
- intravenous infusions are carried out - in order to eliminate violations of water-salt metabolism and acidosis;
- cardiac activity is supported, which suffers in conditions of excess potassium;
- diuresis is stimulated;
- in some cases, peritoneal dialysis is used, when toxic products of nitrogen metabolism are removed by washing with solutions of the abdominal cavity through installed drains, and the peritoneum at the same time acts as a dialysis membrane, this increases the chances of the kidneys for recovery by reducing the load on them;
- constant monitoring of the condition of the cat, the biochemical composition of the blood, the volume of excreted urine, cardiac activity is carried out.
The outcomes of the acute form can be both complete preservation of the functional capabilities of the kidneys, if therapy was carried out in full and on time, and the formation of chronic kidney failure, if the damage was irreversible in a large number of nephrons. In cases when it is not possible to restore kidney function at an acceptable level, the question of carrying out programmed hemodialysis for the cat, as well as kidney transplantation, is decided, which is possible in a small number of veterinary clinics. Otherwise, the death of the pet will occur.
In stationary conditions, treatment of chronic renal failure is carried out when the course of the disease worsens and systemic complications appear.
Treatment of acute renal failure is carried out only in a hospital
Home treatment
At home, only chronic renal failure is treated according to the prescription of a veterinarian. There remains a need for frequent visits to the clinic for control tests, doctor's examination and changes in the drug regimen depending on the results achieved.
Use of medications
Treatment regimens for chronic renal failure are characterized by variability, high individuality and syndromic orientation. Each individual cat may have its own treatment regimen aimed at correcting its prevailing disorders:
- uremia, a state of intoxication with products of nitrogen metabolism - correction of uremia is carried out using a diet with a low protein content; between meals, the cat can be injected subcutaneously with Ringer's solution or saline (0.9% NaCl) in a volume of 20-40 ml per kg of body weight, divided into 2-3 injections per day;
-
increased content of phosphorus in the blood (hyperphosphatemia) - in addition to diet, phosphate binders are used - substances that bind phosphorus entering the intestine (drugs are given with food):
- Almagel Neo;
- Nephrodin;
- Ipakitin;
- Renal;
- an increase in the level of the parathyroid hormone (secondary parathyroidism) - to correct the level of parathyroid hormone, the veterinarian may prescribe calcitriol preparations
-
vomiting - with an attack of indomitable vomiting, metoclapromide (Cerucal) is prescribed - but it is not constantly used; blockers of histamine receptors are included in the therapy regimen:
- Famotidine;
- Cimetidine;
- Ranitidine;
-
anemia - to correct anemia it is prescribed:
- recombinant erythropoietin;
- ferrous sulfate (after starting therapy with erythropoietin);
-
acidosis - alkalizing components are included in the feed:
- bicarbonate of soda;
- potassium citrate;
-
the formation of arterial hypertension, mainly due to vasospasm - drugs that lower the level of blood pressure are used only in the absence of dehydration:
- Amlodipine;
- Enalapril;
- disturbances in the balance of potassium - add potassium gluconate or potassium chloride to the feed, carrying out its regular monitoring in blood serum;
-
antibiotics are used to treat the underlying disease that caused renal failure, or to treat a secondary bacterial infection:
- Sinulox;
- Baytril;
-
for constipation, laxatives based on lactulose are used:
- Duphalac;
- Lactusan;
-
with uremic stomatitis, agents for local antimicrobial therapy are used:
- Metrogyl Denta;
- Holisal;
-
phytopreparations and amino acid preparations are used to maintain kidney function:
- Lespenephril;
- Lespeflan;
- Ketosteril;
- Hofitol;
- Kanephron;
- additionally use vitamins, corticosteroids, diuretics, antioxidants, protease inhibitors, hepatoprotectors, sedatives and other agents - if indicated.
Table: An overview of drugs used to treat kidney failure
| A drug | Structure | Operating principle | Admission rules | Cost, rubles |
| Saline | 0.9% sodium chloride solution | Isotonic crystalloid solution, used to replenish fluid deficiency and reduce the manifestations of uremia |
|
22 (200 ml) |
| Almagel Neo | Algeldrat | It is used for the irreversible binding of phosphorus ions from food; also protects the gastric mucosa in uremic gastritis | 1 ml per kg of body weight; divided into 2 doses, give one hour after meals | 189 |
| Kvamatel | Famotidine | Suppresses gastric secretion | 1 mg / kg once a day | 155 |
| Erythrostim, Epocrine | Recombinant erythropoietin | Stimulates the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow | 50-100 U s / c 2-3 times a week | 2775 |
| Amlodipine | Amlodipine | Blocks calcium channels, causing vasodilation and lowering blood pressure | 0.625-1.25 mg once a day | 12 |
| Sinulox |
|
Broad-spectrum antibiotic | 8.75 mg per kg of body weight once a day for a course of 3-5 days | 910 |
| Duphalac | Lactulose |
Laxative:
|
0.5 ml of the drug per kg of body weight 2 times a day | 292 (200 ml) |
| Metrogyl Denta | Metronidazole | Topical Antimicrobial Gel | Local application to defects of the mucous membrane 3-4 times a day | 207 |
| Lespenephril |
|
|
|
115 |
Photo Gallery: Medicines for Treating Renal Failure in Cats
-

Sinulox suspension - Sinulox is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used in the case of bacterial complications in renal failure
-

Kvamatel - Kvamatel - a remedy for the treatment of peptic ulcer from the group of H2 histamine receptor blockers
-

Almagel Neo - Almagel Neo belongs to the group of antacids and is a drug that helps to reduce the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
-

Duphalac - Duphalac stimulates intestinal peristalsis
-

Metrogyl Denta - Metrogyl Denta is used for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
-

Amlodipine - Amlodipine relaxes vascular smooth muscle and lowers blood pressure
The use of folk remedies
Herbal medicine has a beneficial effect on the condition of the pet, but its use must be coordinated with the veterinarian:
-
Infusion of birch leaves - has a diuretic effect:
- Pour 1 tablespoon of crushed dry leaves with a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour in a water bath.
- Filter the infusion after cooling.
- Ask the cat 1.7 ml per kg of body weight, divided into 2 doses per day.
-
Dandelion root infusion:
- Grind 10 g of dandelion roots, pour a glass of boiling water and place in a water bath for 15 minutes.
- Filter and give the cat 1 ml per kg of body weight 30 minutes before feeding 3-4 times a day.
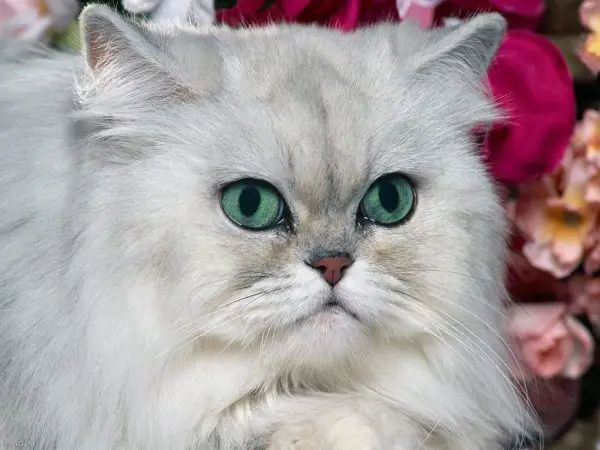

Persian cats have a hereditary predisposition to the development of renal failure
Diet
Diet has a primary role in correcting adverse effects caused by renal failure. To alleviate the symptoms of uremia in food, the protein content is lowered when the urea content increases by more than 10-15 mmol / l; at the same time, the daily protein intake by a cat should not be higher than 3.8-4.5 g / kg of body weight. The protein content in dry feed should not exceed 26-32%.
It is also important to reduce the phosphorus content in the food of a sick pet, since its concentration in the blood naturally increases with the progression of uremia and has an additional damaging effect both on the residual kidney function and on the entire body, especially on the bones and the central nervous system. Phosphorus intake should be limited to 65-85 mg / kg of body weight per day and should be ensured that its content in dry food does not exceed 0.5%.
In a cat's diet, it is necessary to limit sodium as much as possible, as it increases blood pressure.
When fed natural foods, cats are given:
- chicken breasts;
- turkey;
- a rabbit;
- vegetables.
Since it is impossible to control the chemical composition of the ingredients of natural food, and control of the protein and phosphorus content in food with uremia is crucial, it is strongly recommended to transfer the cat to a ready-made veterinary diet:
- Royal Canin Renal;
- Hill's Prescription Diet K / D;
- Eucanuba Renal Formula;
- Purina Veterinary Diets NF;
- Farmina Vet Life Renal.
All veterinary feeds are produced exclusively using original equipment at the developer's premises, so you can trust their quality. The lines contain both dry and wet products. The range of veterinary feeds allows you to choose the right one for the discerning pet. They contain vitamins, polyunsaturated acids and antioxidants necessary to keep your cat healthy.

Hill's Prescription Diet K / D helps prolong and significantly improve the quality of life of animals by reducing the progression of clinical signs of kidney disease
Video: treatment of chronic renal failure in animals
Care rules
Caring for a sick pet is difficult, but very important for the success of treatment and maintaining the quality of life of the cat. It consists of compliance with the following rules:
- compliance with the veterinarian's prescriptions;
- feeding the cat only veterinary food; to increase attractiveness in the absence of appetite, you can offer heated wet food (the cat must eat, even if you have to feed him from his hand);
- providing the cat with plenty of water, the animal must drink (sometimes cats are more willing to use drinking fountains), limiting the amount of fluid consumed will lead to dehydration and an increase in intoxication;
- keeping a pet in a warm room without drafts;
- restrictions on the freedom of movement of the cat (excluding free range);
- if possible, protecting the animal from stress;
- regular testing, since the doctor is guided by them when selecting drugs for the treatment regimen, as well as regular visits to the veterinarian;
- careful observation of the condition of the cat, keeping a diary.
Features of the treatment of pregnant cats and kittens
Kidney failure in a pregnant mother cat may appear due to:
- compression of the ureters by the uterus and impaired urine outflow;
- exacerbation of an undetected disease of the genitourinary system;
- disorders of hormonal regulation due to changes in the ratio of progesterone and vasopressin during pregnancy.
If you suspect renal failure in a mother cat, an emergency veterinarian consultation, examination of the pet and its treatment is necessary. A decision can be made in the operative delivery in the interests of the cat, or natural childbirth followed by artificial feeding of kittens. The cat is given diuretics, solutions are injected subcutaneously, antibiotics are prescribed if necessary, and diuresis is stimulated.
After giving birth, the cat should receive a veterinary diet. Renal failure in pregnant and newly-born cats is often mistaken for eclampsia (a disease that causes high blood pressure to rise). It is necessary to check the functional state of the kidneys in a cat, if its pregnancy is planned, and exclude animals with pathology from breeding.
Therapy for renal failure in kittens is carried out in the same way as in adult animals, but the prognosis in babies is much worse, both because of the predominance of kidney developmental abnormalities in them as a cause of the disease, and because of weak compensatory capabilities if renal failure complicated the course of the general disease. Therefore, if you suspect kidney failure in a kitten, a visit to the veterinarian should be urgent.

In a pregnant cat, renal failure may result from the ureter being squeezed by the uterus.
Prevention of renal failure
Measures to prevent kidney failure include:
- preventive examinations by a veterinarian and regular control tests, especially in cats over 7 years old;
- timely detection and treatment of common acute and chronic diseases;
- identification and treatment of foci of chronic infection, especially in the oral cavity - gingivitis, odontogenic abscesses;
- timely detection and treatment of diseases of the excretory system;
- exclusion of the cat eating poisons, medicines, poisonous plants;
- prohibition of self-medication, since medications prescribed without the knowledge of a doctor can cause irreversible damage to the kidneys;
-
good nutrition of the cat, this will help to avoid urolithiasis - the main cause of kidney failure in cats:
- if the cat eats dry food, then it should be a holistic or premium level;
- if a cat eats natural food, then the basis of its nutrition should be low-fat varieties of meat, fish should rarely be given;
- timely vaccination - will help protect the cat from serious infectious diseases, complicated by renal failure;
- timely deworming - will avoid a decrease in the cat's immunity and its exhaustion;
- Ensuring free access to clean drinking water for the cat, especially when feeding on dry food - to prevent dehydration and its damaging effects on the kidneys.
Veterinarian recommendations
Renal failure, both acute and chronic, is always a complication of the existing disease. The acute form of renal failure is an emergency, but it is potentially reversible and is always treated in a hospital. The chronic form is incurable and prone to slow progression; diet and therapy of both renal failure itself and the disease that caused it can significantly slow down its outcome. With early detection and proper care, a cat can live a long life.
Recommended:
Leukemia (viral Leukemia) In Cats: Causes, Main Symptoms Of The Disease, Treatment And Prognosis Of Survival, Recommendations Of Veterinarians

Causes of viral leukemia in cats Infection routes. How does the disease manifest? Diagnostics and treatment. Forecast. Preventive measures. Veterinarian recommendations
Immunodeficiency In Cats: Which Virus Causes The Disease, Main Symptoms, Treatment And Prognosis Of Survival, Recommendations Of Veterinarians

The causative agent of viral immunodeficiency in cats. Infection routes. How it manifests itself. Diagnostics. Treatment and care. Review of drugs. Forecast, prevention
Eosinophilic Granuloma In Cats: Symptoms And Treatment At Home, Prevention And Recommendations Of Veterinarians

How does eosinophilic granuloma of cats look and proceed? Causes, diagnosis, prevention and treatment methods. Veterinarian recommendations
Enteritis In Cats: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment (including At Home), Prevention, Recommendations Of Veterinarians

What is viral enteritis. Infection routes. Types of the disease. When to see your veterinarian. How to treat at home. Prevention. Doctor's advice
Diseases Of The Eyes In Cats: Photos Of Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment (including At Home), Recommendations Of Veterinarians

What eye diseases are found in cats? How do they manifest. Treatment rules. Animal care during therapy. Prevention. Veterinarian recommendations
