
Table of contents:
- Author Bailey Albertson albertson@usefultipsdiy.com.
- Public 2024-01-17 22:26.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 07:32.
Do-it-yourself greenhouse made of timber and polycarbonate: from the choice of wood to the sheathing of the frame

When, before building a summer cottage greenhouse, future owners take into account both the price, durability and complexity of the installation, the choice in most cases falls on a structure made of wooden beams and polycarbonate. Even 2-3 teenagers can build such a greenhouse, and yields can be obtained in it no worse than in a glass one. It remains only to decide on the design and purchase the necessary materials.
Content
-
1 Greenhouse frame made of timber: features and nuances of choice
- 1.1 Photo examples of greenhouses made of timber and polycarbonate
- 1.2 Comparative table of the advantages and disadvantages of a wooden frame
- 1.3 Material selection
- 1.4 Cooking wood
- 1.5 Video: Making wood impregnation with your own hands
-
2 Assembling and installing the frame with your own hands
- 2.1 Making the foundation
-
2.2 Building the frame
- 2.2.1 Making a glued arch
- 2.2.2 Making a type-setting arch
- 2.2.3 Assembling the frame on the foundation
- 2.2.4 Making the door to the greenhouse
- 2.2.5 Face machining
-
3 Sheathing with polycarbonate
-
3.0.1 Table of the ratio of polycarbonate thickness and thermal conductivity coefficient
- 3.1 Video report on the manufacture of a greenhouse made of wood and polycarbonate
-
Greenhouse frame made of timber: features and nuances of choice
Working with wood is much easier than working with metal, even high school students are taught this. Therefore, any summer resident with a minimum of tools is capable of creating a small structure from a bar.
Photo examples of greenhouses made of timber and polycarbonate
-

Excellent greenhouse with a gable roof - A neatly executed greenhouse looks solid and expensive
-

Greenhouse house - A greenhouse in the form of a small house is the most popular option for a summer cottage greenhouse
-

Vaulted greenhouse - The design of the vaulted greenhouse can be improved with vents under the ceiling
-

Greenhouse from the inside - Internal partitions in the greenhouse can be made of the same polycarbonate
Comparative table of the advantages and disadvantages of a wooden frame
| Benefits | Minuses |
|---|---|
| Low price compared to metal | Begins to break down faster than metal counterparts |
| Installation without professional tools | Requires careful preparation of the material and care of the finished structure |
| Material available, available on the market in a wide range | The wooden frame looks more massive than the metal one due to the increased thickness of the supporting elements |
| Repair of the structure is simple, the replacement parts are made by hand | Maximum service life - 7-8 years |
| Compatible with all finishing materials for greenhouses: foil, polycarbonate, glass | |
| The material is environmentally friendly, processing with safe home remedies is possible | |
| Allows you to create designs of any size |
Material selection

Pine, larch and oak can be easily distinguished by color and pattern of annual rings.
The main guarantee of the durability and reliability of the greenhouse is the correct selection of wood for the frame. Most often used:
- Larch. Only such exotic species as teak, puikando and mahogany (mahogany) are capable of surpassing it in moisture resistance, but even an oligarch will not use them for a greenhouse. Larch grows in our climate, but it is extremely resistant to high temperatures and humidity. The only disadvantage of this wood is its high price, so it is used only by those for whom the naturalness of the material is more important than cost.
- Oak. The wood of this tree is very dense and is not prone to deformation due to moisture. Despite this, he still needs a protective impregnation (if you expect a long service life). Oak is cheaper than larch, but not every summer resident can afford its price. If finances permit, the lower part of the frame should be made of oak.
- Pine. Due to its low price and natural antiseptic properties, pine is the most popular material for greenhouse frames. Before starting construction, this material must be treated with a protective impregnation against premature decay, bugs and other damage.
The cheapest greenhouse can be obtained if you use spruce for the frame. But since it is even less dense than pine, only a small structure (up to 3x5 m) can be made with it, and it is best to put it on a strip foundation.
Cooking wood
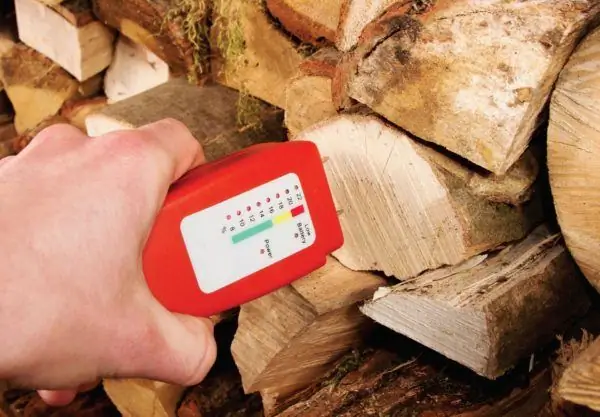

Wood moisture measurement
First of all, you should pay attention to the moisture content of the wood. It is best to buy material with a water content of 12% to 18%, a more moist timber will dry out under the sun on its own and cracks will appear on it. Therefore, it is important not to immediately skimp on quality.

Industrial machines allow each board to dry safely and evenly
If you cut down a tree in the country and plan to use it to build a greenhouse, the prepared boards will need to be dried. If a stable humidity is maintained in the country house, you can simply leave the boards and timber in the room. They will need to be monitored from time to time so that the material does not bend during the drying process. The quality of such drying is much worse than industrial, but if the greenhouse is small and you have not yet had the experience of building such structures, you can use wood. In 5-6 years, you will be able to plan your new plant house more carefully and thoughtfully.

All open surfaces of the timber must be thoroughly smeared with a protective liquid.
Also, do not forget about bio-fire protection. The purchased material is soaked in a protective liquid for several hours, and then thoroughly dried. Some compounds can be simply applied to the wood surface with a brush or spray. The most popular manufacturers of such impregnations are Senezh, Neomid, Pirilax, Woodmaster.
Video: Making wood impregnation with your own hands
If traces of dirt appear on the wood after transportation or processing at home, they should be removed with a plane or emery cloth (depending on the depth of penetration). Since the greenhouse cover will be transparent, without such preparation, the frame will look untidy, and putrefactive bacteria may also appear in the dirt.
DIY assembly and installation of the frame
Polycarbonate greenhouses are best made arched. In this case, the polymer sheets can be bent rather than cut. This makes it easier to cut the material and there are fewer seams that need to be sealed (compared to a gable house).
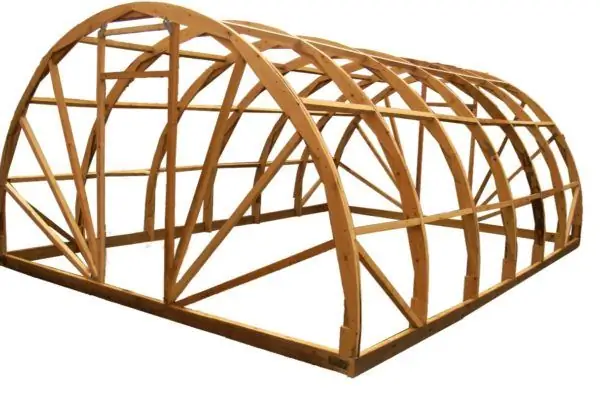

This version of the frame is decorated with radius end beams
The attached drawing can only be used for orientation, since the exact parameters of your greenhouse should depend on the size of the area allocated for it, the number and type of crops grown and the planned budget. This design can be modified by increasing / decreasing the size of the arch, as well as the number of spans between the ends.
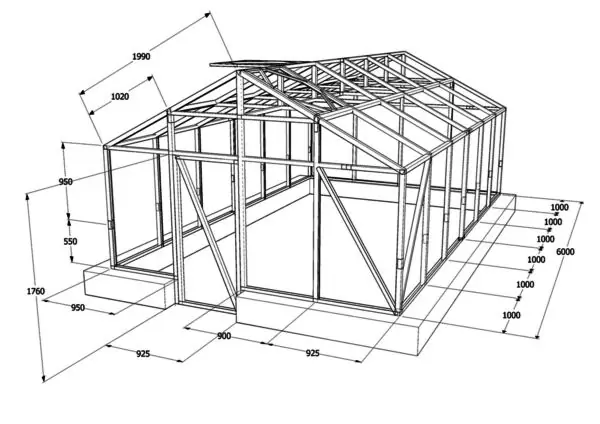
Detailed drawing of a greenhouse made of timber with a gable roof
This version of the greenhouse is the most popular, despite the fact that it is more expensive and more difficult to install than an arched one.
Making the foundation
The most reliable option is to create a strip foundation by digging a trench 40-50 cm deep around the perimeter of the greenhouse, then filling it with a mixture of rubble and concrete and erecting a 20-30 cm high wall. For this:
-
Dig a trench only 10-25 cm deep, being careful not to damage the roots of nearby shrubs or flowers. (You cannot make a greenhouse under the trees, as its inhabitants will not receive enough light). Rope markings will help to keep the lines straight and to the correct width throughout the ditch.

Greenhouse trench Trench for the foundation of the greenhouse, marked with ropes
-
Fill the ditch with greasy clay and compact it. It is not difficult to recognize oily clay: it is easy to sculpt smooth balls and elastic sausages from it. This will be the first waterproofing layer.

Trench clay Trench clay can be dug in any other corner of the site
-
Place a coarse sand cushion in the trench as if it were a garden path. When the sand is filled up, pour water generously over it. So the pillow will immediately shrink and your future foundation will not squirm after the rain.

Layers Basic layers: soil, clay, sand, waterproofing
-
Cover the greenhouse perimeter with a dense polyethylene film or waterproofing membrane / agrofibre / geotextile. This will protect the greenhouse base timber from excessive moisture. Many people use roofing material for the same purpose, but it should be borne in mind that this material is not environmentally friendly and, when placed in the ground, serves only 2-3 years.

Geotextile Geotextiles from different manufacturers differ in properties, so when choosing, you should consult with the seller
-
Place 4 beams in the trench according to the size of the sides of the greenhouse and with a section of 130x130 cm or 150x150. If there are no beams of a suitable size, you can connect several boards with hairpins in 4-5 places so that each board stands on the end. Corner fastenings are best done using the “foot” or “tenon in the groove” method. The grooves are cut with a conventional gasoline or hand saw.

Fastening the tenon into the groove Corner connection of a bar by the "thorn in a groove" method
-
To increase the rigidity of the structure inside the frame, fix the metal corners on the self-tapping screws. The same is done when the corner is connected with a bracket.

Metal corner The metal corner in the type-setting beams should be fastened with the longest wood screws
-
The foundation box must lie strictly horizontally, the top must be 5 cm above ground level. Be sure to check its correct location using a building level. For this purpose, a water level with a long tube and two flasks is best suited.

Water level You will need an assistant to use the water level
-
In addition, long pins (50-70 cm) driven into the ground from a thick-walled pipe or reinforcement will help to fix the position of the foundation. For them, you need to drill a hole of a slightly smaller diameter in the wood and drive the supports into the ground at the corners of the wooden box.

Armature The pins are easy to make from a reinforcing bar with a section of 10-12 mm
The wooden foundation obtained as a result of the described actions can be used as a strapping for a wooden frame. If you were making a tape, it would have to be waterproofed and in the same way fixed a rectangle of beams - a strapping.
Those who plan to heat the greenhouse by passing smoke through pipes under the beds should make trenches under them and lay pipes before arranging a wooden foundation.
We build a frame
Consider the process of building a frame using the example of an arched greenhouse, which is most suitable for sheathing with polycarbonate. In addition, such a design suffers less from the weight of the snow and is not afraid of severe frosts.
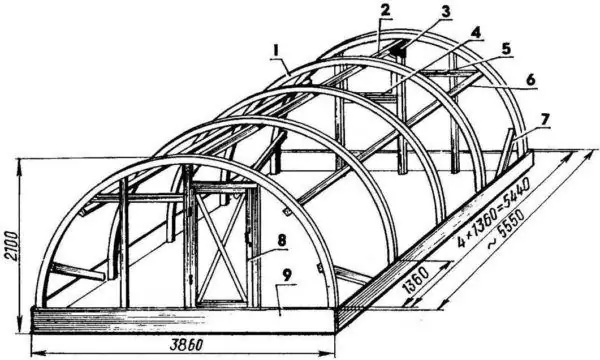
Drawing of the frame of an arched greenhouse from a bar, dimensions in mm
Legend in the picture:
- frame arch;
- upper longitudinal bar;
- corner fasteners;
- end jumper;
- jumper connecting the longitudinal bar and the butt;
- lateral longitudinal bar;
- corner brace;
- door frame;
- wooden foundation / strapping.
The ends can be reinforced not with vertical and horizontal beams, but with radii.
The most time consuming process in the manufacture of such a greenhouse is the creation of arches. They can be made in one piece, by gluing separate thin strips, or typesetting.
Making a glued arch
First you need to make a stand for bending a tree. To do this, it is enough to make markings on a piece of plywood by drawing an arc of the size required for your greenhouse, and then drive wooden pegs along the perimeter in a checkerboard pattern.
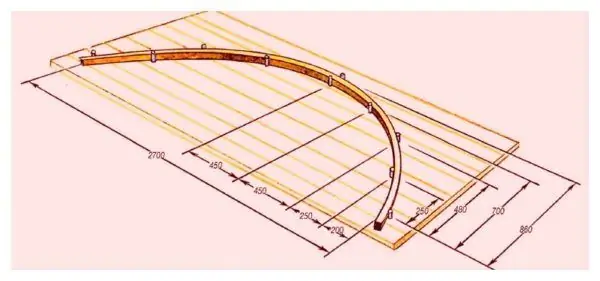
Such a simple stand for bending the planks is easy to make with your own hands.
The arches can serve as the walls and roof of the greenhouse, as in the attached greenhouse drawing. Then the arc should be high with a large bend, it will be more difficult for a beginner to make it. But you can make low (50-70 cm) walls in the greenhouse and put arcs on them. Such arcs are flatter and shorter, making them much easier.
An arched roof is typical for industrial greenhouses, for a home one needs to proportionally reduce all sizes
Let's start making a glued wooden arch:
-
Take a board with a high moisture content (it will be easier to bend) 5-10 mm thick, 50-70 mm wide and equal to the calculated length of your arch with an allowance of 10-15 cm. bent position. The board may not be solid, but glued PVA from several layers, so the design will be even more reliable.

Arch stand The shallow arch can be fixed at just three points
-
On one stand, you can fix several planks at once, laying beams of the same width between the boards. The support bars are easily fixed to the stand with self-tapping screws.

Two arcs on the stand Clamps will additionally help fix the arcs
The planks will need to be dried on the stand for several days, depending on the amount of glue used, as well as the initial moisture content of the wood. It is better to prepare arches for the spring greenhouse in winter in order to have time to build the required number of arches without defects.
Making a type-setting arch
For a stacked arch, you don't need a stand or bending skills. To get a reliable massive arc, follow the instructions:
-
Cut out an arch template of the required size with the required bending radius from fiberboard or any other dense sheet material. A simple homemade compass will help to accurately round off.

Homemade compasses Such a compass can be made in 2-3 minutes from scrap materials
-
Make a rough arch from the boards, holding them together as shown. After that, circle the template with a pencil and additionally reinforce the places where the fastener will be too thin after cutting.

Arch frame By increasing the number of boards, you can make an arch of any size
-
Use a jigsaw to trim off any excess boards. It is necessary to round only the outer part of the arch to which the polycarbonate will be attached. The inner one can be left as it is, it will be even more reliable.

Greenhouse made of compound arches Arcs rounded on both sides look sleeker
The number of arches required depends on the length of the planned greenhouse. When calculating, keep in mind that the recommended distance between the arcs is 135 cm.
Assembling the frame on the foundation
If your arches are ready, you can start installing them on the ground:
-
Attach the end arches to the foundation bars using steel corners and additionally secure them with slopes.

Fastening the timber These ways of connecting corners can be combined
-
Install other arches in the same way and combine them with 5x5 cm bars. The length of the bar should be equal to the distance between the arcs. Use the method of fastening with self-tapping screws into the end through the arch, and also fix the corners at the top and bottom of the strip (4 pieces per segment). Instead, you can use one longitudinal beam, but you will need to make cuts in it for each arch.

Steel fittings Such fittings will greatly facilitate the installation of crossbars.
-
Using one of the described methods, secure the upper and another side longitudinal strip of the frame. If the greenhouse is tall, there should be at least five longitudinal bars (whole or assembled from fragments).

Greenhouse frame made of wood The frame with strapping can be assembled separately and transferred to the foundation ready
-
At one of the ends, make a strapping for the subsequent fastening of a window (one or more).

Window Calculate the size of the window in the greenhouse taking into account the preferences of the crops grown
As a result, you should have a stable frame made of arches. If necessary, further strengthen it by adding braces or another series of longitudinal strips.
Making a greenhouse door
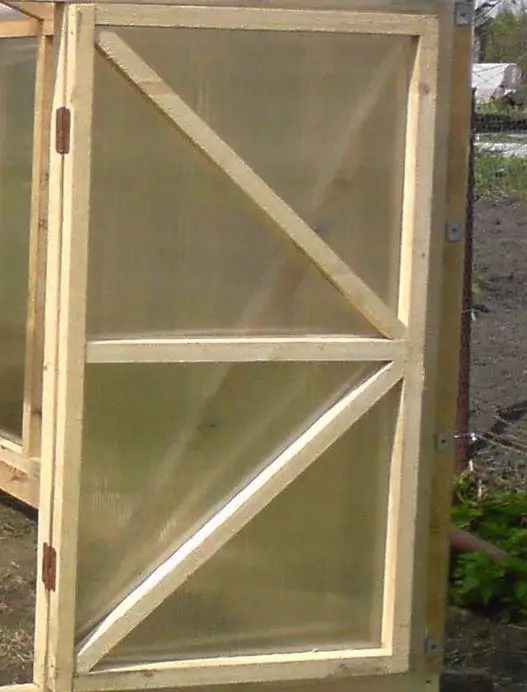

The door to the greenhouse made of timber
The door for the greenhouse can be made from bars of the same cross section, fastening them in the corners with self-tapping screws for wood. For the stability of the geometry, it is important to add braces that form a triangle (as in the picture) or a cross. The size of the door depends on your preference and build. But it is better not to make the sash too large, so as not to violate the temperature regime of the greenhouse at the entrance.
At the end of the assembly, be sure to check the correct geometry of the door with a building level, and then remove the burrs from the bar with a grinder or sandpaper.
End machining
The ends of an arched greenhouse can be decorated either with a structure of vertical and horizontal racks, or with radius strips. The second option is simple to implement and looks more aesthetically pleasing.
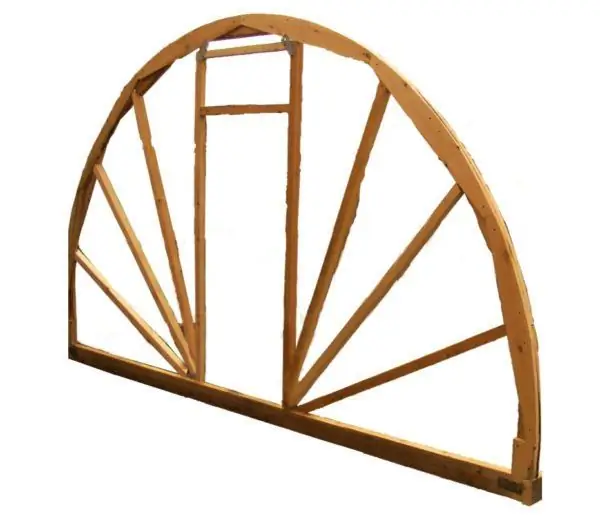

Example of an end with a door
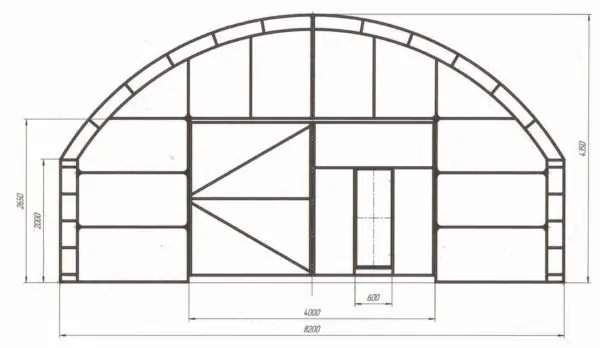
If you do not have planks of the required length, the end with the door is designed as follows.
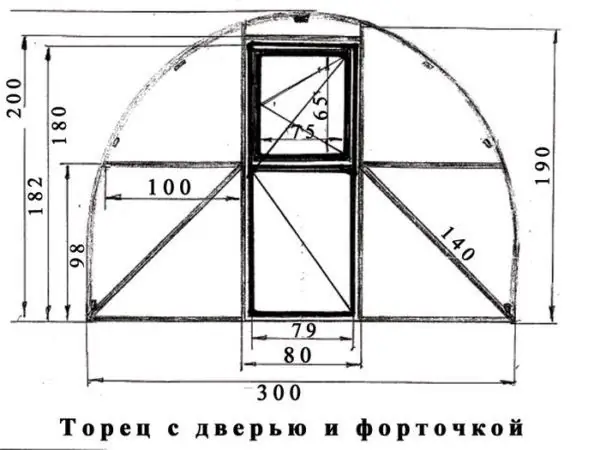
Greenhouse end drawing with approximate dimensions
Polycarbonate sheathing
The finished frame can be sheathed with polycarbonate. Since this material is quite expensive and does not always tolerate shock loads well, it is better to sew up the greenhouse wall with boards to the height of the beds. This way you will definitely not damage the plastic with an accidental blow with a shovel or a rake. The quality of the boards does not really matter, the main thing is that they are impregnated with fire-biological protection and, when connected, do not create large cracks (otherwise, the earth will wake up through them).
When buying, pay attention to the thickness of the polycarbonate sheet: thin ones are easier to bend
Table of the ratio of polycarbonate thickness and thermal conductivity coefficient
| Sheet thickness, mm | Thermal conductivity, W / m 2 |
|---|---|
| 4 | 3.9 |
| 6 | 3.6 |
| 8 | 3.4 |
| ten | 3.1 |
| 16 | 2,3 |
The further north your region is, the thicker the polycarbonate you need to buy for the greenhouse. This is especially important if you plan to plant your plants in winter or early spring.
It is possible to start installing polycarbonate only on a calm, windless day, since the material has a high wind capacity. Otherwise, the semi-fixed sheet can be blown off the frame even with a slight gust.
Then follow the instructions:
-
Fasten the lower part of the split profile along the arch at a distance of the width of the polycarbonate sheet. Install a sheet of honeycomb polymer into the groove and secure it with special self-tapping screws with a waterproofing collar. The hole for the self-tapping screw must be made with a drill of slightly smaller diameter. Continue this process until the greenhouse is completely covered.

Polycarbonate installation diagram Polycarbonate is best mounted using specialized hardware.
-
Cover open sheet cells with punched tape and end profile to protect the vulnerable edge from damage.

Profiles U-shaped profile is needed for the ends, H-shaped can be used for joints
-
Install the top covers of the split profiles and secure them with self-tapping screws. Ordinary roofing, which is used for the installation of metal tiles, is suitable.

Self-tapping screws for wood Self-tapping screws for wood with a rubber seal are suitable for you
To make a wooden greenhouse with a polycarbonate coating, you will need the following tools:
- wooden pegs and a coil of rope for marking the territory for the foundation;
- chainsaw, hand saw or jigsaw for cutting wood and grooving;
- a screwdriver for fastening wooden fragments and fixing metal corners;
- building level to control the position of frame elements;
- water level to control the position of the foundation;
- a sander or sandpaper for wood processing.
Video report on the manufacture of a greenhouse made of wood and polycarbonate
Using the enclosed instructions, you can improve your garden plot and build a comfortable greenhouse that can last 7-15 years.
Recommended:
How To Build A Polycarbonate Greenhouse With Your Own Hands: Step-by-step Instructions For Assembly And Installation With Photos, Videos And Drawings

Types of polycarbonate greenhouse structures, recommendations for the choice of materials, schemes. Step-by-step instructions for making your own hands, photos and videos
How To Build A Glass Greenhouse With Your Own Hands: Which Is Better, Glass Or Polycarbonate, Step-by-step Instructions With Photos, Videos And Drawings

Making a glass greenhouse with your own hands: material features, recommendations for choosing glass, calculations. Detailed construction technology. Useful Tips
Do-it-yourself Foundation For A Greenhouse Made Of Polycarbonate And Other Materials - Step-by-step Instructions With Photos, Videos And Drawings

Types of foundations suitable for greenhouse construction. Step-by-step instructions for the construction of a structure from a bar, reinforced concrete and other materials
Installing A Sink In The Bathroom: How To Properly Install A Washbasin With Your Own Hands, At What Height To Fix And Other Installation Features

Types of bathroom sinks. The sequence of installation, connection to water supply and sewerage, performance check. Errors and methods of their elimination
How To Build A Polycarbonate Greenhouse With Your Own Hands - Step By Step Instructions With Photos, Videos And Drawings
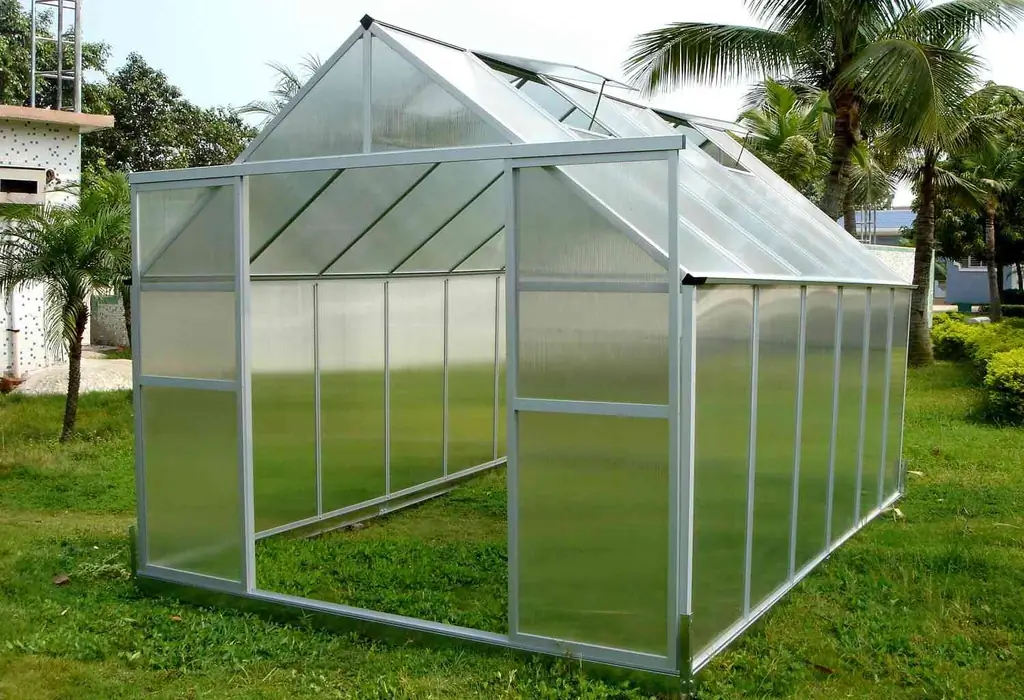

How to make a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands: the choice of materials and shape of the structure, requirements for the structure, installation and rules
