
Table of contents:
- Author Bailey Albertson albertson@usefultipsdiy.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 12:53.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:41.
Tomato leaves turn yellow: how to save the planting?

Sometimes, soon after planting even a beautiful seedling of tomatoes, her leaves suddenly begin to turn yellow. And if some of the reasons for this phenomenon can be easily eliminated, the plants can be returned to normal existence, then sometimes yellowing can be a sign of serious trouble, the fight against which will take a lot of time and effort.
Content
-
1 Why do tomato leaves turn yellow
- 1.1 Post-transplant stress
- 1.2 Malfunctioning root system
- 1.3 Low temperature
- 1.4 Damage to the root system when loosening
- 1.5 Lack or excess of moisture
- 1.6 Lack of nutrients
- 1.7 Diseases and pests
-
2 Methods of dealing with the problem
2.1 Video: what to do when the leaves of tomatoes turn yellow
- 3 Reviews
Why do tomato leaves turn yellow?
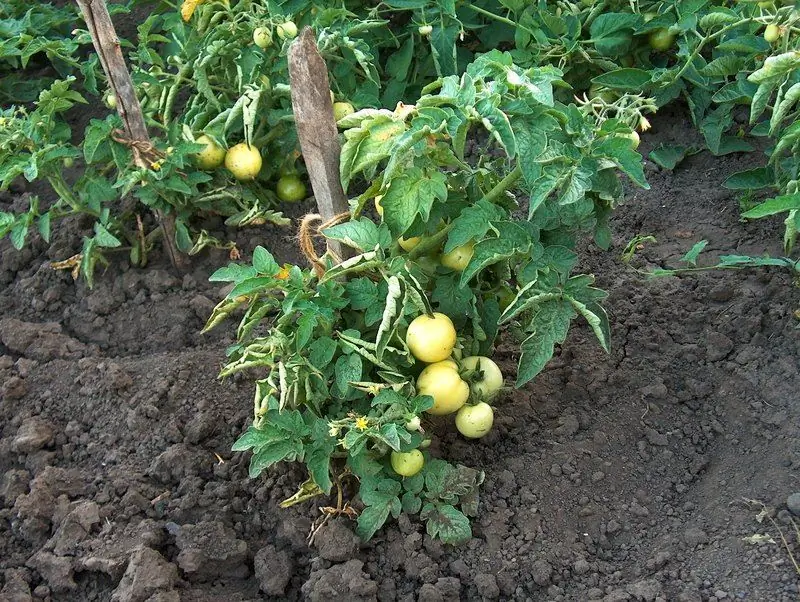
If the yellowing of the leaves is slight, especially only at the bottom of the bush, this is not very scary. It is bad if almost the entire plant turns yellow.
Post-transplant stress
Often, literally a few days after planting seedlings in the ground, its lower leaves turn yellow. This may well be considered a natural phenomenon associated with a sharp change in the living conditions of tomatoes. Indeed, in a city apartment, seedlings lived in close quarters - in a small box or very small cups. The bush is used to eating from its own roots according to one "recipe", and with the increase in living space, its diet changes. In this situation, the plant tries to "feed" the upper part of the bush to maintain viability, while the lower leaves are temporarily lacking in nutrition. Most likely, after a few days, a pair of the lowest leaves will fall off, and if this does not happen, you can cut them off yourself: good seedlings have enough vegetative mass, a lot of healthy leaves will soon grow.

Yellowing of only the lower leaves in young plants is the smallest problem
Improper functioning of the root system
When planting seedlings together with an earthen lump (or even better with a peat pot), she will hardly notice a change in conditions: the condition of the roots will practically remain the same. They will simply have the opportunity to grow further - in depth and to the sides. However, if you had to plant seedlings with almost bare roots, after buying from common boxes, then when planting in the ground, the roots will take up completely unusual positions for themselves, intertwine, tear, etc. In this case, naturally, the bush will significantly weaken and until they grow new roots, it will lack nourishment. In this case, yellowing is possible not only of the lower leaves, but also of many of the following.

The use of peat pots guarantees the integrity of the seedling roots
Low temperature
It is not always possible to plant tomatoes in the garden with the onset of real summer. Often after a very warm May comes the cool June and tomatoes if not quite adapted to a bed, and not resumed rapid growth, a cool night when the temperature approaches almost 0 on C, will be enough to seriously plant to supercool. It will not necessarily die (at low positive temperatures, tomatoes can die only under the influence of strong winds), but it will hurt for a long time. And the first sign will be yellowing of the leaves, many of which will subsequently disappear. Therefore, when the cold weather returns, leaving tomatoes without shelter is unacceptable.
Damage to the root system when loosening
The tomato bed is loosened after watering as long as possible, until the bushes are closed. But loosening too deep can lead to chopping off several important roots, and this happens, as a rule, already with rather large bushes. Since they are quite strong by this time, a decrease in the number of roots will slightly affect the condition of the bush, but the lower leaves may well turn yellow. In literally a week, new roots will grow, so this phenomenon will not affect the health of the main part of the bush.

The hoe must be used very carefully.
Lack or excess of moisture
Tomatoes are among crops that need watering to a moderate degree. When the soil dries out, the leaves can turn yellow and even fall off, especially when it comes to cracks in the surface layer. Indeed, at the same time, overheating of the roots by the sun's rays is added to dehydration.
However, excess moisture is perhaps the most common cause of yellow leaves. When the soil is swamped, oxygen does not get to the roots, without which the normal existence of the plant is impossible. The trouble begins with yellowing of the leaves, and if the flow of moisture continues without measure, the tomatoes may die.
Lack of nutrients
In principle, from a sharp lack of any of the main nutrients (nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus), yellowing of tomato leaves can occur, but most often this is nitrogen starvation. This can happen at any stage of plant development, except, perhaps, during the ripening period of the fruit: at this time, nitrogen is practically not required for tomatoes. Yellowing can also occur due to a severe lack of certain trace elements (for example, molybdenum or manganese), but these cases are relatively rare.
Diseases and pests
Among the many diseases of tomatoes, only fusarium wilting leads to a clear yellowing of the leaves. This is a very dangerous fungal disease, the causative agent of which can be present in seeds, soil, and organic fertilizers. The disease begins with the root system, but the gardener sees its manifestations already with yellowing and further wilting of the stem and foliage. Late blight rarely begins with yellowing, usually brown spots appear immediately.

In some diseases, the leaves turn yellow first.
With the yellowing of the leaves, external manifestations of damage to the root system of tomatoes by pests can begin: wireworm or bear. Usually they spoil the roots so badly that young plants can no longer be saved.
Methods to deal with the problem
If only the lower leaves have turned yellow, you can not worry too much, but measures should still be taken. When we are talking about recently planted seedlings, and all the reasons given are clearly absent, you just need to cut off these leaves over time, the process of development of the bush will almost not stop. When the lower leaves turn yellow at the time of fruit ripening, this is also normal. After all, the bush itself is trying to get rid of what the gardener himself should have done: at this time, the lower leaves only interfere, drawing off the plant's resources instead of directing them to the ripening of tomatoes. It is better to cut these leaves with scissors, although they often do it by hand; it is important not to damage the stem during the operation.
But in any case, you should make sure that yellowing of the leaves is a physiological process, and not associated with flaws in agricultural technology (with massive yellowing, physiology cannot be talked about). Therefore, you should find the reason and try to eliminate it:
- establish an irrigation regime (water only in the morning or evening, not too cold water, without fanaticism);
- to carry out top dressing (possibly extraordinary, including foliar);
- when diagnosing "fusarium", you can try to save some of the plants by treating them with Trichodermin or Previkur according to the instructions for the drug.
In severe cases, there are, of course, no guarantees of maintaining full health, and even more of a high harvest, but at least something should remain in the beds, one must try.
Video: what to do when tomato leaves turn yellow
Reviews
The yellowing of the leaves of tomatoes, especially the lower ones, is not always a big problem, sometimes it is a natural process. But with the severity of the problem, each time it is necessary to seriously understand in order to take measures, if possible, and save the plants and the crop.
Recommended:
How To Feed Cucumbers In The Open Field If The Leaves Turn Yellow And In Other Cases

Top dressing with slow growth of cucumbers. How to fertilize if the leaves turn yellow. How to feed in a polycarbonate greenhouse. Feeding with yeast. Instructions. Video
Why Windows In Houses, Including Plastic Ones, Sweat In Winter, What To Do

Reasons for fogging windows in winter. Why does moisture collect on insulating glass. How to fix the problem
Why Are Wisdom Teeth Needed And Should They Be Removed, Including On The Lower Jaw
Functions of wisdom teeth. Why are they called that. When to remove wisdom teeth
Is It Necessary To Give Up The Lower Shelf On The Train To Passengers From The Upper One, Including Pregnant Women And Children

Is it necessary to let train passengers from the upper shelf to the lower one, to give way to them: what does the law and the rules for the carriage of passengers say
Salt From Late Blight On Tomatoes: How To Properly Process Tomatoes

What is the mechanism of protection of tomatoes from late blight with the help of table salt. How often should plants be treated, what should be the concentration of the solution
