
Table of contents:
- Author Bailey Albertson albertson@usefultipsdiy.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 12:53.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 07:32.
Soft roll roofing: device, installation features, recommendations for operation and repair

Soft roll roofing does not differ in either high strength or durability, while remaining quite in demand. Today, when installing this type of coating, a wide range of materials are used that differ in laying technology.
Content
-
1 Soft roll roofing: features and characteristics
-
1.1 Roofing materials for soft roll roofing
- 1.1.1 Traditional materials
- 1.1.2 Bituminous-polymer
- 1.1.3 Single-layer membranes
-
- 2 Tool
- 3 Installation of a soft roll roof
-
4 Features of the installation of a soft roof
-
4.1 Installation of roofing material
- 4.1.1 Placing the deposited material
- 4.1.2 Bonding roofing material (cold installation)
- 4.1.3 Laying soft roofing materials on pitched roofs
- 4.1.4 Laying a single layer membrane
- 4.1.5 Video: how to weld a roll roof
- 4.2 Errors when installing a soft roll roof
-
-
5 Features of operation of roll roofing
- 5.1 Life expectancy
- 5.2 Repair of soft roofs
- 5.3 Using an electric air heater in the repair of a soft roll roof
- 5.4 Video: DIY repair of a soft roll roof
Soft roll roofing: features and characteristics
The popularity of roll roofing materials is explained by the following positive qualities:
- low cost;
- high speed of installation;
- light weight;
- lack of characteristic noise during rain and strong winds.
If we consider a soft roof as the only possible coating option for a flat roof with a concrete base, then several more advantages can be added:
- no calculation is required, as is the case with the rafter system;
- installation is simple (the construction of a truss structure is a much more complex process);
- the flat roof with a soft roll cover is walkable.
However, one has to reckon with the following disadvantages:
- low strength;
- relatively short service life;
- unremarkable appearance.

Soft roll cover ideal for flat roofs
Roofing materials for soft roll roofing
If earlier the term "roll roofing materials" united under itself only roofing material and roofing felt, then by now this list has expanded significantly.
Traditional materials
This is the already mentioned roofing material and roofing felt. In the production of the first, bitumen is used, the second - tar. These materials are applied from both sides to cardboard, which is a base or frame.
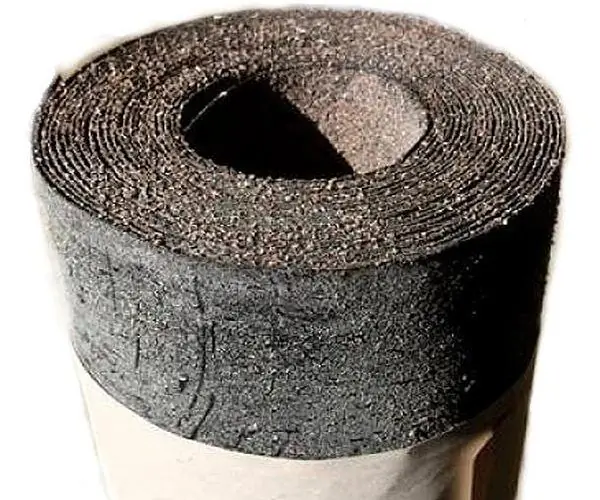

Roofing paper is a cardboard impregnated with coal or shale tar
Roofing felt and roofing felt attract a low cost, but they have many weak points, since the strength of the cardboard base is extremely low:
- bitumen and tar, under the influence of solar radiation and temperature changes, quickly lose their elasticity and crack;
- for the same reasons, cracks quickly appear in the mastics used for gluing panels;
- the material has a porous surface, and therefore has a low frost resistance (it is relatively quickly destroyed during freeze-thaw cycles of water that has got into the pores).
The listed disadvantages together make traditional materials extremely short-lived - they last no more than 5-7 years.
Bituminous-polymer
New generation roll materials. During their production, various polymer additives are added to bitumen, for example, styrene-butadiene-styrene, which significantly improve its properties:
- reduce the number and size of pores, thereby increasing frost resistance;
- increase plasticity, as a result of which the material does not crack longer;
- provide higher resistance to solar radiation and other atmospheric factors;
- allow to lay materials without the use of mastics - by fusing (when heated, the surface of the panel becomes sticky).
In addition, much stronger fiberglass, fiberglass and polyester are used instead of cardboard.

The basis can be fiberglass, polyester or fiberglass
There are, so to speak, variations on the theme:
-
Materials in which aluminum foil is used instead of stone powder: metalloizol, foilgoizol, etc.

Folgoizol Folgoizol is laid on top of the insulation
-
Materials that have no basis at all (baseless): isol, brizol, etc. They are made from a mixture of bitumen and rubber.

Brizol In addition to petroleum bitumen and rubber, brizol contains asbestos and plasticizers
The purchase of bitumen-polymer materials will have to spend more money than the roofing material would cost, but due to the longer service life (up to 15 years), the total cost of maintaining the roof for the entire period of operation is reduced by 2 times.
Some disadvantages for both bituminous and bitumen-polymer materials are common:
- a stone powder or a layer of foil is required as protection from solar radiation;
- the maximum permissible roof slope is 25% (with a greater steepness, the coating softened in the heat will slip);
- materials have to be stacked in several layers.
Single layer membranes
In the manufacture of these roll materials, bitumen is not used at all. The raw materials are various types of rubber and petroleum resin.
In terms of their properties, membranes are significantly superior to bitumen-polymer materials:
- due to high elasticity and resistance to all negative environmental factors without exception, they have a service life of 25 years;
- fit in just one layer;
- can be produced in rolls of very large width (up to 15 m), which significantly reduces the number of joints on the roof.
Long service life in combination with single-layer installation allows to reduce the cost of roof maintenance for the entire period of operation by 4 times compared to a conventional bitumen roofing (roofing felt)
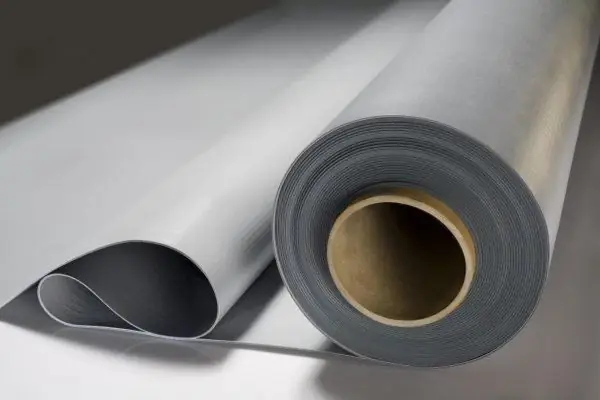

Polymer single layer membranes are high strength roofing
Tool
The master who has taken up the device of a soft roll roof will need the following:
- A well-sharpened construction knife - it is necessary for cutting panels.
- Special hook, which is convenient for unrolling bales.
- In the case of application of deposited materials - gas or kerosene burner. It is more convenient to work with gas and it costs less, but it is also more dangerous and therefore requires skillful handling. It is better for a beginner to opt for a kerosene burner.
- Maklovitsy. This is the name of the special brushes used for applying mastics. If they were not in the arsenal, you can use an old broom for the same purpose.
- Roller for pressing down glued panels.
- If the membrane is to be laid - a building hair dryer.
- A broom or broom for removing debris from the roof.
- A set of tools for making mortar and laying the screed: shovel, trowel, as a rule, rack level, beacons.
-
Perforator and dowels (roll materials have to be fixed mechanically in places).

Hand tool Hand tools for roofing and insulation work: a - metal spatula; b - awl saddlery; c - brush for applying mastic; d - paddle with rubber insert; d - plaster hammer; e - a tank for mastic with a capacity of 20 liters; g - a bucket with a capacity of 15 liters; h - thermos with a capacity of 25 l
In addition to tools, you will need containers for the preparation and delivery of mastics and cement-sand mortar to the roof.
Soft roll roofing device
A soft roof is a multi-layer structure, which includes (from bottom to top):
- The base is a reinforced concrete slab.
- Vapor barrier film. Protects the insulation from the steam coming from the downstream premises (the base always has some vapor permeability). If it gets into the insulation, the steam would condense, which can lead, firstly, to a decrease in the thermal resistance of the roof, and secondly, to its destruction as a result of moisture freezing.
- Insulation. In this capacity, materials should be used that can withstand large loads without significant deformations: mineral wool plates with a density of 90 kg / m 3, extruded polystyrene foam or less effective, but cheap expanded clay.
- Cement-sand screed.
-
Waterproofing coating made of roll materials. All types, except for single-layer membranes, are stacked in several layers: with a slope of more than 15% - in two layers; between 5 and 15% - in three layers; less than 5% - in 4-5 layers.

Soft Roll Roofing Pie The soft roll roof is laid on a continuous sheathing
On a pitched roof, the role of the base is played by a continuous crate (flooring made of plywood or boards laid without a gap), while the screed is not used, and the insulation is placed under the base - between the rafters
Features of installing a soft roof
If the roof of the building is flat, then first of all you need to decide how the slope will be performed on it. This is the name of the formation of one or more inclined surfaces (with a slope of 1-5 °), along which water will flow into the drainage system. You can do the following:
- If the building has not yet been completed: lay the slabs with a slope, making the front wall two brick rows higher than the back one. The method is suitable for a garage or small outbuilding, which are covered with one slab.
- Lay the insulation with the desired slope. There are special wedge-shaped boards made of extruded polystyrene foam and mineral wool. They are laid in a second layer on top of ordinary boards. Expanded clay, slag and any other bulk material can be given a slope using a rule, having previously installed beacons. This method is not very good, since wedge-shaped slabs are expensive and not always available, and expanded clay is pressed through over time, so that the slope may disappear. They resort to it when the slabs have already been laid and at the same time are designed only for the snow load.
-
Lay the screed with a slope. The best way, but only suitable if the slabs are capable of withstanding, in addition to the calculated snow load, the weight of a thick screed layer.

Flat roof slope The purpose of the slope is to prevent the formation of water accumulations on the roof surface
In extreme cases, under the insulation they make a bed of sand and perform the slope with its help.
A soft roof on a flat roof is formed as follows:
- Slots, sinks and cracks on the slabs are sealed with mortar or repair compound.
- While the repair composition is drying, storm inlets, funnels and other elements of the drainage system are installed.
- Next, a vapor barrier film is laid on top of the slabs. The overlap should be 10-15 cm, and it should be glued with double-sided tape. The edges of the film are brought onto the parapet and other vertical elements so that they are above the entire future roofing cake. If it is decided to use glassine as a vapor barrier, then it must be glued with mastic.
-
After that, the heat insulator is laid. Plates of expanded polystyrene or mineral wool can be attached with disc dowels (they have a large cap), but it is better to glue them, since metal fasteners will contribute to heat leakage.

Laying thermal insulation on a flat roof For insulation of a flat roof, mineral wool or extruded polystyrene foam is most often used
- A reinforcing mesh is placed on top of the insulation, and then a screed is placed. If it is decided to perform the spreading with its help, beacons must be placed before laying. The screed layer thickness is from 2 to 7 cm. The screed must be divided into 6x6 m squares, between which expansion joints must be made 5 mm wide.
- The corners along the vertical elements must be filled with a solution to a width and height of 10 cm, so that the transition between the horizontal and vertical planes becomes smooth.
-
After 4-6 hours after laying the screed, it is covered with a primer, which is bitumen dissolved in kerosene in a 1: 1 ratio (it is called a primer).

Diagram of the device of a soft roll roof on a flat roof The insulation is laid in two layers: the upper, thinner one, prevents the formation of cold bridges at the joints of the main thermal insulation boards
Primers and mastics can be purchased ready-made at the hardware store
After that, you can start laying the roll material.
Installation of roofing material
Before covering the entire roof surface, do the following:
- The expansion joints in the screed are glued with roll material. The strips should be 15 cm wide, bituminous mastic acts as an adhesive.
- Also, with the help of bitumen mastic, square areas around the water intake funnels measuring 70x70 cm are glued.
- Parapets and other vertical elements are glued in the following way: first, one fragment is glued with a 25 cm approach to the vertical element. The upper edge is attached to the vertical element with dowels or nails, and the lower horizontal part is glued to the screed. The second fragment is glued with an overhang of 35 cm, while the upper edge is rolled into a 5 cm roller and pressed against the vertical element with a mounting plate.
After that, the main roofing material is laid.
With roof slopes up to 15%, the rolls are unrolled parallel to the cornice (ridge), starting from the lowest point, with greater steepness (pitched roofs) - perpendicularly
The methods of laying hardfacing and non-melting (cold laying) materials are different.
Laying the deposited material
Let's remind that bitumen-polymer materials can be laid by the fusion method. The procedure is as follows:
- The material unfolds completely and fits into place.
- Heat its edge from below with a burner until it becomes shiny. Then it is pressed against the base, which must also be warmed up. Roll weldment should not be overheated too much - this will make it less durable.
-
Having secured the edge, the roll is wound up.

Laying the deposited material Overheating of the deposited material must not be allowed
Then they act like this:
- one worker simultaneously heats the bottom surface of the roll and the base area in front of it with a burner;
- the second, operating with a special hook, rolls out the roll;
- the third, with the help of a roller, firmly presses the panel to the base.
If the heating was carried out correctly, the rolled-out roll will drive a side of bitumen with a height of about 2 cm in front of it. After pressing with the roller, the bitumen will protrude from under the edges of the panel.
Bonding roofing material (cold laying)
Traditional materials - roofing felt and roofing felt - are glued with mastics. The composition of the mastic must correspond to the composition of the binder in the roofing material: the roofing material must be glued with bituminous mastic, only tar.
The installation of the material is as follows:
- One day before the start of work, the rolls are unrolled and left to rest. If there is no free space for this, then the rolls must be rewound so that the material is bent in the opposite direction.
- After delivery to the installation site, the roll is rolled out, trying on, then rolled from both sides to the middle.
- Gluing is performed, moving from the middle, first in one direction, then in the other. One worker smears the base with mastic in front of the roll, processing about 1.5 square meters at a time. m, the second one unrolls the roll and presses it to the base.
The sheets are laid with an overlap:
- with a roof slope of up to 5 °: at least 10 cm in all layers;
-
over 5 °: in the inner (lining) layers - 7-8 cm, in the outer layer - 10-15 cm.

The size of the overlap of the rolled roof panels Overlapping of different layers must not be allowed
The overlaps on the ends of the panels are always 15 cm and in different layers should not lie one on top of the other, they need to be shifted by at least 10 cm.
Laying soft roofing materials on a pitched roof
If the pitched roof has a slope of up to 15%, the installation of the roofing material is carried out in the same way as on a flat roof. In this case, the edges of the upper panels overlap the ridge, and then another strip of material is glued on top of it.
At slopes of more than 15%, the rolls are turned perpendicular to the ridge, while the end of the 30-40 cm long panel should be thrown over the ridge. On the opposite slope, laying is done in the same way.
A hanging edge about 15 cm long is left below, which is then wound under the cornice and nailed to it with roofing nails.
Laying a single layer membrane
Installation of this type of coating is much easier. The membrane is glued, screwed with screws or dowels, or simply sprinkled with rubble. The mechanical method of fastening is the most popular because it is much more expensive to attach the membrane to the adhesive.
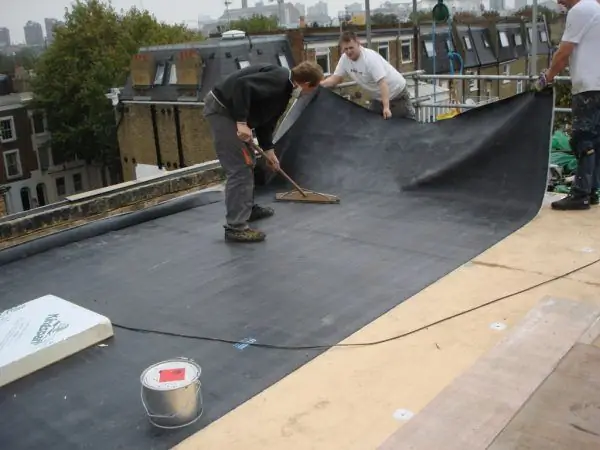

Membrane width does not allow installation work alone
As already mentioned, the width of the membrane roll can reach 15 m, so on small roofs, the coating is seamless. With a large building area, the coating must be assembled from separate panels. They are welded to each other using a special heater. You can also warm up the edges of the panels with the help of a construction hair dryer, after which they are rolled with a special roller for welding. The hair dryer is also used when decorating the adjoining of the coating to vertical elements.
Video: how to weld a roll roof
Errors when installing a soft roll roof
The following actions lead to a significant reduction in the quality of the roofing coating:
- Overheating of bitumen-polymer material during fusion. As a result, the coating loses its elasticity, which leads to the rapid opening of cracks.
-
Lack of thorough rolling of the material, as a result of which voids remain under it. Water vapor in such bubbles will condense during a cold snap, then moisture will destroy the material during several freeze-thaw cycles. If it is no longer possible to transfer the material, the voids are pierced and then opened with a cruciform incision. The resulting triangles are folded back, mastic is poured under them, then the material is glued and poured again with mastic on top. If the edge was poorly pressed, it must be separated from the base with a spatula and glued or melted again.

Bloated roofing Air bubbles can form due to lack of vapor barrier
-
Laying panels with a bias. When the panels are laid unevenly, in some places the overlap turns out to be too large, but in others it is completely absent. Water is likely to penetrate into the joints without overlap. If during installation it becomes obvious that the panel is skewed, the part that has not yet been laid (it is coiled into a roll) must be cut off, corrected and laid in the correct direction, having completed an end overlap of 15 cm.

Soft roof defect Water can enter the joints without overlap
- Moving through the material just laid. The mastic and the weld material that have not yet cooled down are soft, therefore dents form in them when walking. In the future, water will collect in these dents, which will lead either to leaks or to the destruction of the roofing material due to freezing.
- Poor fixation of the edge of the coating. In strong winds, the tearing off of the roof begins precisely from the edge, so it must be very carefully glued and filled with bitumen or mechanically fixed.
-
Incorrect roll-off. A serious defect, as a result of which water will not be completely removed from the coating. Where it remains, rot or vegetation may appear, leaks will begin to appear over time, and with the onset of frost, the roofing cake will be destroyed by ice. To check if the slope is correct, the roof must be filled with water before laying the last layer. Places where puddles remain are outlined with chalk, then dried and sealed with a piece of rolled material 1 mm thick.

Roof vegetation Moss or vegetation may appear in places where moisture accumulates
- Lack of reliable pasting of vertical elements. The adjoining of the roof to vertical elements is a very critical area in which leaks are likely to occur. Therefore, when waterproofing them, it is very important to act in accordance with the instructions and remember that an additional layer of material in such a place will never be superfluous.
Features of the operation of roll roofing
As already mentioned, strength is not among the advantages of a roll roof, therefore, it must be inspected twice a year. Attention should be drawn to the following phenomena:
- cracks;
- detachment;
- bloating;
- pits, dents and other similar defects;
- areas from which the powder has been washed away (a large amount of powder in the gutters should also cause concern);
- puddles or indirect signs of their periodic presence - areas with fungus, rot or vegetation.

When examining, special attention is paid to the places where the roofing carpet mates with various structures.
If you find any of the above, you need to schedule repairs for the near future. The sooner it is completed, the less costly it will turn out, since defects in the soft roof progress rather quickly. Vegetation must be removed immediately, as it quickly destroys the roofing cake with its root system.
It is necessary to clean the soft roof from snow and leaves very carefully, preferably using not a metal, but a wooden shovel, even better - rubberized. To avoid contact of the tool with the coating, it is better to brush off the snow not completely, leaving a layer about 5 cm thick.
If branches and other heavy objects are found on bitumen-containing roofing material, they must be immediately removed, since over time they will sink into the coating, deforming it and violating its integrity.
Life expectancy
Under normal conditions and with proper operation, the soft roll roof does not require repair:
- with a coating of bituminous and tar materials (roofing felt, roofing felt) - 5-7 years;
- with bitumen-polymer coating - 15 years;
- with a single layer membrane - 25 years.
Soft roof repair
Such a roof is usually restored in the following ways:
- In the presence of delamination: remove dirt from the cavity, then dry it with a building hairdryer and carefully glue the material with mastic. From above, the repaired area is also poured with a layer of mastic.
- If blisters are present: open with a cruciform incision and check if water has penetrated to the underlying layer. If it penetrates, it is cut out and so act until it reaches the dry layer. After that, the fragments cut to the size of the holes are glued in one after the other in the same quantity as the layers were cut. Finally, the top layer, cut crosswise, is carefully glued, after which a patch is glued to the repaired area. The patch should be 10-15 cm larger than the defect in each direction. From above it is poured with a layer of bitumen, and the mixture must be rolled out with a roller so that it lies in a thicker layer on the edges of the patch.
-
When cracks are found: the damaged area is cut down, they get to the dry layer and then a patch is applied using the above technology.

Soft roll roof repair technology Small damage to the roofing material can be patched
Many experts consider local repair to be ineffective, since in addition to defects visible on the surface, hidden defects can form in the roofing cake, the location of which cannot be determined. "Old repair" is considered more reliable, when, instead of installing separate patches, the old roof is completely covered with roll material in one layer. Of course, such repairs cannot be carried out indefinitely, since the bearing capacity of the floor slabs is limited. The number of layers laid on them should not exceed 8.
If the roof is worn out by more than 40%, patching of individual sections and even “old repair” becomes inappropriate. It is necessary to resort to overhaul, which consists of at least replacing the roofing, and in the most difficult cases, replacing the entire roofing pie, starting with the vapor barrier.
Using an electric air heater in the repair of a soft roll roof
One of the conditions for a high-quality repair is the absence of moisture in the area of its implementation. All layers of the roofing can be dried by heating them with radiant streams that can penetrate into the thickness of the material. The structure of the layers is preserved in its original form.
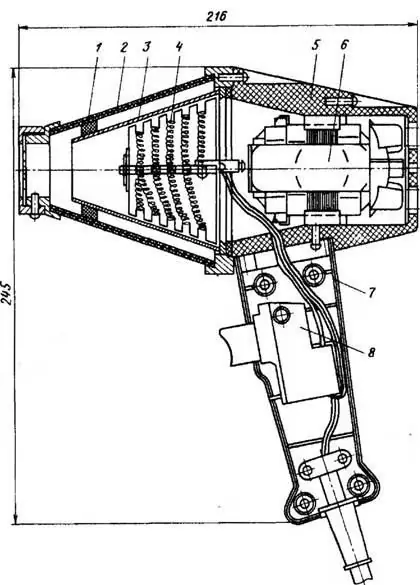
Electric air heater device: 1 - support sleeve; 2 - outer cone; 3 - inner cone; 4 - heating element; 5 - case; 6 - electric motor; 7 - handle; 8 - switch
The roofing material is heated to a temperature of 200 ° C, which leads to the melting of the bitumen.
This technology is applicable only to soft roll-type materials: if bitumen shingles are heated to such a temperature, its sheets will lose their shape
Video: do-it-yourself soft roll roof repair
Of all the roofing materials, rolls are the cheapest, while they fit much faster than any other. It is only necessary to carefully observe the installation technology, especially if there is a slight slope on the roof. If everything is done correctly - the slope is completed and overlaps are observed - the soft roof will diligently serve the entire period assigned to it.
Recommended:
Straw Roofing, Including Its Structure, Installation And Operation Features, As Well As How To Do It Yourself

Characteristics of a thatched roof, its advantages, installation features. How to make a straw roof with your own hands. Operating rules and repair
Roofing From Vulture Panels, Its Structure And Main Elements, As Well As Features Of Installation And Operation

Brief information about roofing SIP panels. Design features of roofs assembled from multi-layer products. Sandwich panel installation rules
Roofing From A Profiled Sheet, Including The Features Of Its Design And Operation, Repair, As Well As How To Avoid Mistakes During Installation

What kind of profiled sheet can be used for the roof. DIY cold and insulated roof device. What mistakes are possible. Features of operation and repair
Roll Roofing, Including The Features Of Its Construction, Operation And Repair, As Well As How To Avoid Mistakes During Installation

The difference between roll roofing and modern and Soviet counterparts. Can I use roll roofing on a pitched roof? How to install it and when to repair it
Roofing Cake For A Soft Roof, As Well As The Features Of Its Structure And Installation, Depending On The Type Of Roof And The Purpose Of The Room

What is a cake under a soft roof. Features of its device and installation. How to arrange a roofing cake from roll and piece materials
