
Table of contents:
- Author Bailey Albertson albertson@usefultipsdiy.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 12:53.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:41.
Is Down syndrome inherited?

Everyone has probably heard and has an idea of Down syndrome. But does this view coincide with reality? For example, is Down syndrome inherited?
What is Down syndrome and how is it spread
When talking about Down syndrome, it is important to understand that this is not a disease in the conventional sense of the word. Down syndrome is a genetic disorder in which the set of human chromosomes, as a rule, is represented by 47 chromosomes instead of 46.

Down syndrome human karyotype contains an extra chromosome
The pathology in question is not acquired: the deviation occurs at the time of conception. If a cell that carries a set of 24 chromosomes (normally 23) participates in fertilization, the fetus develops Down syndrome. Moreover, in 90% of cases, the extra chromosome is carried by the female cell, and only in 10% of cases - by the male. Factors such as the presence of bad habits in parents, illness during pregnancy, etc., do not affect the occurrence of the syndrome.
There are several forms of the syndrome:
- trisomy (caused by nondisjunction of chromosomes during the formation of the parent's sex cells and entails the defeat of all cells of the child's body);
- mosaicism (caused by nondisjunction of chromosomes in the embryonic cell and affects only some tissues and organs);
- translocations (caused by the attachment of the shoulder of the 21st chromosome to the shoulder of the 14th, which increases the chance of trisomy during reproduction);
- duplication (caused by duplication of sections of the 21st chromosome as a result of chromosomal rearrangement).
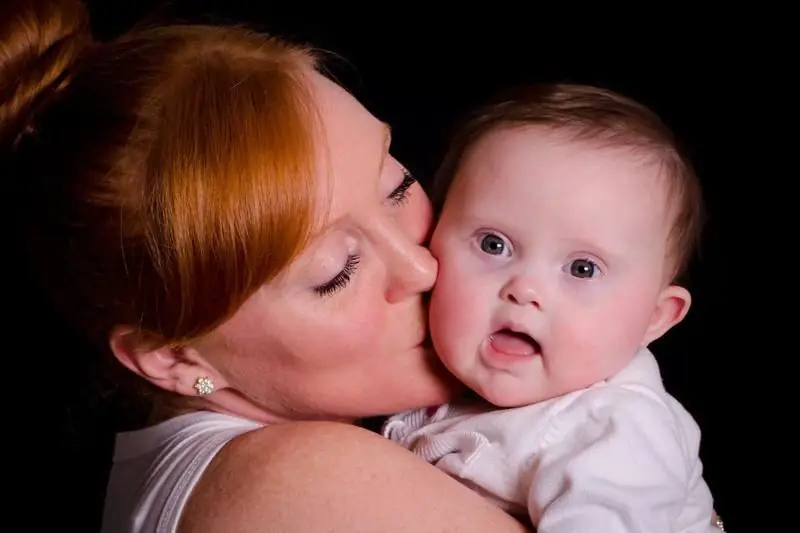
Regardless of the form of the syndrome, its characteristic symptoms are:
- abnormal shortening of the skull;
-
recognizable facial features:
- flat round face;
- slanted eyes;
- epicanthus (third eyelid hanging over the inner corner of the eye);
- flat nose;
- dental abnormalities;
- short nose;
- age spots on the iris;

Recognizable facial features in a child with Down syndrome People with Down syndrome look alike
- short neck;
- small growth;
- increased joint mobility;
- decreased muscle tone;
- short limbs and fingers;
- crooked little finger;
- transverse palmar fold;
- deformation of the chest;
-
the presence of concomitant diseases:
- hearing impairment;
- violation of respiratory activity;
- heart disease:
- leukemia;
- strabismus;
- early cataract, etc.
Moreover, in each case, the set of symptoms is individual. However, all carriers of the syndrome are inherent in kindness, gentleness, patience, ability and love of creativity, for which they are often called "children of the sun."

Down syndrome carriers tend to be surprisingly creative.
According to research data, the most common form of the syndrome is trisomy (about 95% of cases). Mosaicism, translocations and duplications are much less common (3%, 1%, and less than 1% of cases, respectively).
The factors that can lead to the syndrome are:
-
the age of the parents (over 35 for the mother and 45 for the father);

Relationship between maternal age and risk of the syndrome The risk of developing Down syndrome in a child is higher, the higher the age of the mother.
- the age of the maternal grandmother at the time of the birth of her child (mother of a child with the syndrome) - the older she was, the higher the risk of developing the disease in her grandson / granddaughter;
- incest (marriage between blood relatives);
- heredity (1/3 of all cases of the translocation form of the syndrome or no more than 2% of all cases of the disease).
In other words, Down syndrome in 99% of cases is an accidental genetic, but not hereditary anomaly. Every family can face this pathology, regardless of race, lifestyle, financial situation.
Video: Elena Malysheva on Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a serious genetic pathology from which no one is immune. However, with the current level of medicine, it is possible to significantly minimize the risk of the syndrome. If, for some reason, this could not be done, it is important to understand that the syndrome is not a sentence: with proper care, patience, care and love, the carrier of the pathology can lead a normal life and be happy.
Recommended:
How To Crop, Flip, Overlay Music, Slow Down Or Speed Up Video On IPhone

How to process video captured on smartphones or tablets from Apple: crop, rotate or overlay music. Step-by-step instructions included
How To Wash A Down Jacket In A Washing Machine And Is It Possible To Do It

Rules for washing a down jacket at home in a washing machine. The means used. How to rinse and dry a down jacket
What To Do If The Mozila Firefox Browser Slows Down - Reasons And Solutions

Why can Mozilla Firefox slow down? How to return its previous high performance: we use all methods
Is Cancer Inherited
Can cancer be hereditary? What is the likelihood of suffering from cancer if there were cancer patients in the family
Sleep Paralysis: Causes, How To Cause Old Witch Syndrome

Description of sleep paralysis. What a person feels during sleep paralysis. Is he dangerous. Can I call it myself
