
Table of contents:
- Do-it-yourself lathing for corrugated board: we mount quickly and efficiently
- Sheathing for corrugated board and its types
- The size of the crate for corrugated board
- Crate thickness
- Calculation of material for lathing for corrugated board
- Do-it-yourself lathing for corrugated board
- Counter grating for corrugated board
- Author Bailey Albertson albertson@usefultipsdiy.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 12:53.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 07:32.
Do-it-yourself lathing for corrugated board: we mount quickly and efficiently

Roofing sheeting is a sheet covering material with different thickness and height of corrugation. In view of this, the strength of a profiled metal roof depends on the correct choice of the material itself, taking into account the loads for a particular area, as well as on the truss system and the roofing pie, which is part of the sheathing, which is correctly mounted under it.
Content
-
1 Sheathing for corrugated board and its types
-
1.1 Wooden crate for corrugated board
- 1.1.1 Table: recommended pitch of wooden lathing for corrugated board
- 1.1.2 Video: Instant installation of the battens
- 1.1.3 Table: Recommended section of lumber for sheathing for corrugated board
- 1.1.4 Video: Aligning the battens
- 1.2 Metal crate for corrugated board
-
- 2 The size of the crate for corrugated board
- 3 The thickness of the lathing
-
4 Calculation of material for lathing for corrugated board
-
4.1 Solid sheathing
4.1.1 Table: number of boards in 1 m³
- 4.2 Sparse lathing
- 4.3 How to save on crate
-
-
5 Do-it-yourself lathing for corrugated board
5.1 Video: installation of the sheathing for corrugated board
-
6 Counter grating for corrugated board
6.1 Video: counter grill, to do or not
Sheathing for corrugated board and its types
Initially, it may seem that the main element of the roofing structure is the rafters, which transmit the pressure of the roof to the walls and foundation. But one can argue with this, since natural factors - torrential rains, heavy winds and heavy snowfalls - affect precisely the roofing, the basis for which is the crate. Therefore, without exaggeration, it can be called the main part of the roof.
Wooden crate for corrugated board
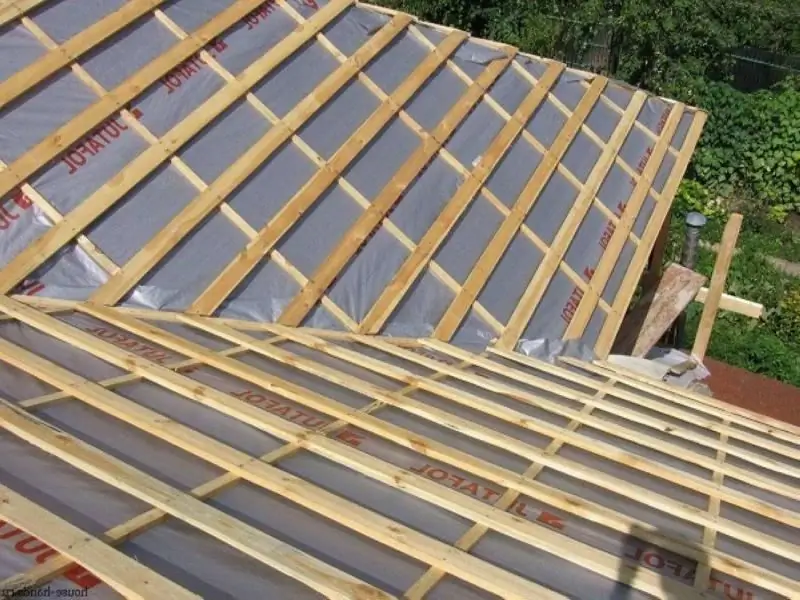
Traditionally, a crate for a metal profile is made of wood (section 6 of SNiP II-26-76 *), using a timber or edged board of conifers of good drying. It is cheaper than metal construction and easier to install.

Most often, the crate for the corrugated board is made of wooden bars and fixed with nails.
Sheathing for corrugated board is of two types.
- Solid - with no more than 2 cm gaps between the boards. It is mainly used for laying low-wave profile coverings.
-
Sparse - with a step according to metal thickness, profile height, roof slope and loads (SNiP 2.01.07-85 *). Despite the fact that the lattice lathing is more difficult to install, it is used more often, since it does not weigh down the roofing structure and allows you to save on lumber.

Types of crate For sheet coverings, they often make a sparse crate, since it does not create unnecessary load and requires less materials
Table: recommended pitch of wooden lathing for corrugated board
| Corrugated board brand | Roof slope, deg. | Sheet thickness, mm | Lathing step, mm |
| S-8 | not less than 15 | 0.5 | solid |
| S-10 | up to 15 | 0.5 | solid |
| more than 15 | 0.5 | up to 300 | |
| S-20 | up to 15 | 0.5-0.7 | solid |
| more than 15 | 0.5- 0.7 | up to 500 | |
| S-21 | up to 15 | 0.5-0.7 | up to 300 |
| more than 15 | 0.5-0.7 | up to 650 | |
| NS-35 | up to 15 | 0.5-0.7 | up to 500 |
| more than 15 | 0.5-0.7 | up to 1000 | |
| N-60 | not less than 8 | 0.7-0.9 | up to 3000 |
| N-75 | not less than 8 | 0.7-0.9 | up to 4000 |
| In regions with strong, frequent winds, it is necessary to reduce the pitch of the sheathing up to halving | |||
In addition to the slope of the roof, the height of the wave and the thickness of the profile covering, the pitch of the lathing also depends on the shape of the roof and the quality of processing of the covering material. Therefore, when choosing, you need to pay attention to the accompanying documentation, which indicates the individual requirements of manufacturers for the installation of their products.
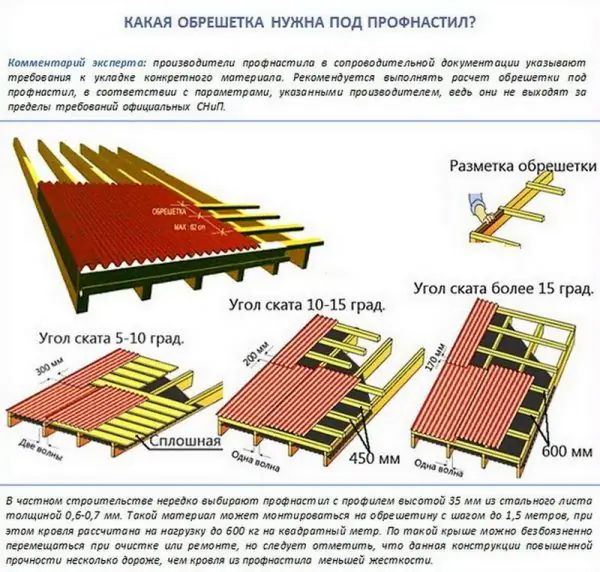
The type of lathing depends on the brand of the corrugated board used and the angle of inclination of the roof, and its pitch is usually negotiated by the manufacturers of the covering material
Video: instant installation of the crate
Taking into account the chosen step of the lathing, focusing on the slope of the roof and the step of the rafters, they select the lumber of the desired section.
Table: recommended section of lumber for sheathing for corrugated board
| Lathing step, mm | Roof slope | |||||
| 1: 1 | 1: 1.5 | 1: 3 or more gentle | ||||
| Rafter pitch 0.9 m | Rafter pitch 1.2 m | Rafter pitch 0.9 m | Rafter pitch 1.2 m | Rafter pitch 0.9 m | Rafter pitch 1.2 m | |
| 250 | 22X100 | 25X100 | 22X100 | 25X100 | 22X100 | 32X100 |
| 300 | 22X100 | 25X100 | 22X100 | 32X100 | 25X100 | 32X100 |
| 400 | 22X100 | 32X100 | 22X100 | 32X100 | 25X100 | 38X100 |
| 450 | 22X100 | 32X100 | 25X100 | 32X100 | 32X100 | 38x100 |
| 600 | 25X100 | 32X100 | 25X100 | 32X100 | 32X100 | 38x100 |
| 750 | 32X100 | 38X100 | 32X100 | 38X100 | 32X100 | 50X100 |
| 900 | 32X100 | 38X100 | 32X100 | 38X100 | 38X100 | 50X100 |
| 1200 | 32X100 | 50X100 | 32X100 | 50X100 | 38X100 | 50X100 |
| 1500 | 50X100 | 50X100 | 50X100 | 50X100 | 50X100 | 50X100 |
All sawn timber before filling the sheathing must be sorted, checked for the quality of the cut, the presence of deformations, bends, knots and moisture (the optimal indicator is 18-20%), and also treated with an antiseptic
The strength and durability of the roof depends on correctly selected sawn timber, so it is not worth saving on them so as not to make unnecessary problems, including:
- poor air circulation in the under-roof space, which provokes the appearance of dampness and mold and the rapid deterioration of all structural elements;
- weakened fastening of profiled sheets and all layers of the roofing cake;
- difficulty with the installation of gable and end strips, as well as shaped and additional elements.
Video: leveling the crate
Metal crate for corrugated board
The rapidly growing building density in recent years has led to a tightening of the regulatory framework, in particular, fire safety rules. In this regard, more and more often the wooden truss structure began to be replaced by a metal one, which has undeniable advantages:
- helps to reduce wind pressure due to a decrease in the total area of the crate;
- provides free access to all roofing elements;
- not prone to rotting and burning;
-
is flawlessly smooth, which is of great importance for the firm fixation of the covering material.

Metal crate for corrugated board Metal lathing is increasingly becoming a profitable alternative to a wooden structure, especially since the installation of metal profile lathing is performed in the usual way
According to SP 31-101-97, steel girders fixed to the supporting elements with a step of 1.5-3 m for unheated buildings or remote Z-girders for heated houses can serve as the basis for a roofing made of corrugated board. Distance runs are installed along the slopes or at an angle of 45 ° to the ridge / cornice and fixed to the lower profiled sheet mounted across the slopes. In order to increase the noise insulation of the metal roof, as well as to break the cold bridges in insulated structures, the standards recommend installing thermal pads over the girders, and use roll materials such as perforated polyethylene film as waterproofing to allow the roof to breathe freely.
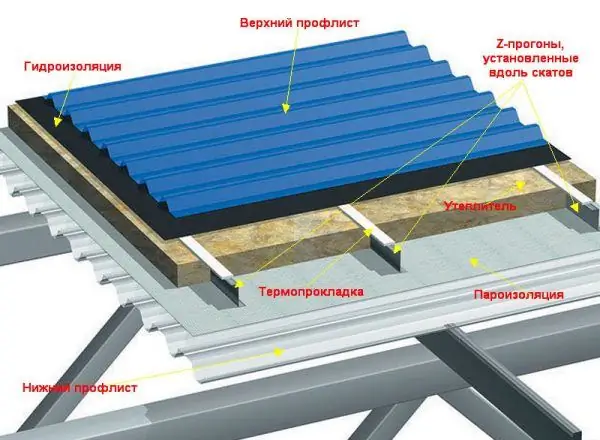
For insulated roofs, distance Z-runs, mounted along the slopes or diagonally, serve as metal lathing
The size of the crate for corrugated board
The size of the crate for corrugated board depends on the roof area, the number of communication outlets and the presence of a drainage system.

The size of the sheathing for the corrugated board depends on the roof area and the availability of an organized external drain, as well as on the number and size of engineering structures on the roof
Let's consider the calculation of this parameter using an example. Initial data - a gable roof with a slope length of 10 m and a height of 8 m, there are three chimneys with dimensions of 0.4X1.2 m each, one ventilation duct with a section of 100X200 mm (cross-sectional area of 0.02 m2), a cornice overhang 40 cm wide (0, 4 m), a typical external drain, an angle of inclination of more than 15 ° and a step of a single-layer lathing corresponding to the slope of the roof 300 mm.
- We calculate the area of the lathing S arr. It is equal to the total area of the roof, excluding chimneys, ventilation ducts and roof windows (if any). When calculating the height of the slopes, it is necessary to take into account the ledges along the eaves over the entire length, plus at least 30 cm for the organization of an external drain.
- According to the initial data, S arr = (10 ∙ 8 ∙ 2) - (0.4 ∙ 1.2 ∙ 3) - 0.02 + (0.4 x ∙ 10 ∙ 2) + (0.3 ∙ 10 ∙ 2) = 160 - 1.44 - 0.02 + 8 + 6 = 172.54 m².
- The total area of the crate is 172.54 m².
According to the level of strength, the crate is made single-layer or two-layer. When choosing a reinforced structure, the area of the lathing for calculating lumber needs to be doubled.
Crate thickness
Depending on the type and size of the roof, as well as the pitch between the rafter joists, lumber of various thicknesses is used.
-
The most common material for wooden lathing is edged board with a section of 22X100 and 25X100 mm. It is affordable, but, unfortunately, not strong enough, therefore it is advisable to use it when erecting light and uncomplicated roofs with a rafter pitch of no more than 600 mm.

Edged board Edged boards with a thickness of 22 and 25 mm are the most demanded lumber for lathing
- A 32X100 mm board is considered universal, which is excellent for stuffing a sparse crate with a gap between the rafters up to 900 mm.
-
Tongue boards 25 and 32 mm thick with a tongue-and-groove connection for solid lathing and calibrated to create a sparse - strong, well-processed, beautiful, but very expensive lumber. Therefore, they are rarely used for filling battens, despite the accuracy of the cut.

Grooved and grooved boards Grooved and calibrated boards are made with high cutting accuracy, however, due to the high cost, they are rarely used for filling the battens.
-
A beam of 50x50 mm is used with a rafter leg pitch of 900 mm to equip complex structures with many decorative and shaping elements. Due to its strength and thickness, it will protect the roof from deflections due to increased pressure on the slopes.

Beam for lathing The lathing made of timber is arranged with a large pitch of rafters and a slope of the roof, as well as when using a covering corrugated board with a high wave, that is, when the roof structure is designed for a significant load
The thickness of the metal lathing depends on the height of the U-shaped steel profile used, which is selected:
- in thickness - in proportion to the length of the spans and the weight of the roofing cake - the longer the spans and the greater the weight, the thicker the profile for the lathing;
- by height - according to the height of the wave of the covering material - the higher the wave height, the higher the profile height should be.
Thus, the thickness of the metal lathing will be equal to the height of the hat profile. The situation is a little different with spacer Z-profiles for run-free construction, which are installed on the edge. In this case, the thickness of the metal lathing is equal to the width of the head of the intermediate profile.
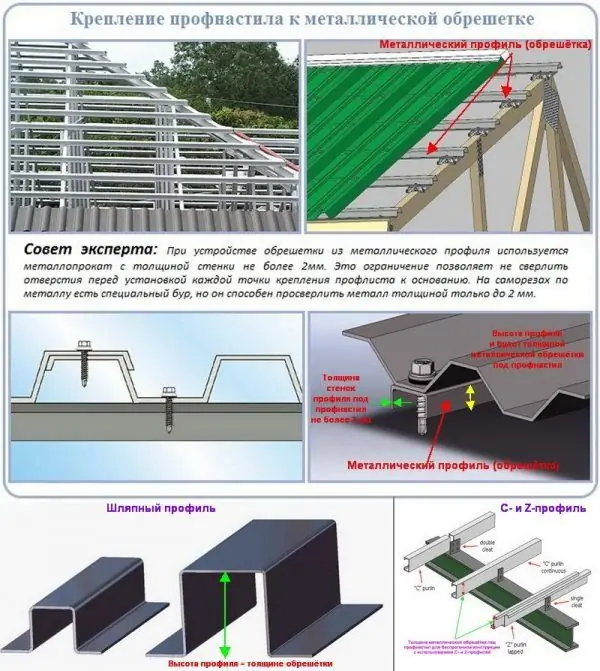
The thickness of the metal crate is equal to the height of the profile used or the width of the head of the C- and Z-profiles when arranging a non-run roof
Calculation of material for lathing for corrugated board
To prevent unnecessary costs for the lathing device, you need to be guided by the working project documentation, which contains all the necessary measurements and a ready-made calculation of the required materials. If the roof project was not drawn up, then you should take measurements yourself - measure the height and length of the slopes, the total length of the ridge lines, edges, valleys and eaves, as well as the width and length of the passages.
Solid crate
To calculate the lumber, we will use a special table and the dimensions of the crate calculated above.
Table: number of boards in 1 m³
| Board dimensions, mm | Volume of one board, m³ | Number of boards in 1 m³, pcs. |
| 22Х100Х6000 | 0.013 | 75.8 |
| 25X100X6000 | 0.015 | 66.6 |
| 25X130X6000 | 0.019 | 51.2 |
| 25X150X6000 | 0.022 | 44.4 |
| 25X200X6000 | 0.030 | 33.3 |
| 30X200X6000 | 0.036 | 27,7 |
| 40X100X6000 | 0.024 | 41.6 |
| 40X150X6000 | 0.036 | 27,7 |
| 40X200X6000 | 0.048 | 20.8 |
| 50X100X6000 | 0.030 | 33.3 |
| 50X150X6000 | 0.045 | 22.2 |
| 50X200X6000 | 0.060 | 16.6 |
|
All values are based on standard board lengths (6 m). To find out the footage (running meters), the number is multiplied by the length of the boards / timber |
||
According to our data, the area of the crate is 172.54 m². Let's say that a board with a section of 22X100X6000 mm is used.
- We find the area of one board by multiplying its width by length: 0.1 ∙ 6 = 0.6 m².
- Determine the required number of boards: N = 172.54 / 0.6 = 287.56 pcs.
- We add to the found quantity a stock of 10%: N = 287.56 ∙ 1.1 ≈ 316 pcs.
- We translate the number of boards 22X100X6000 into cubic or linear meters, since lumber is often sold in these units. From the table we find that 1 m 3 contains 75.8 boards, so the required volume is 316 / 75.8 ≈ 4.17 m³. The footage is calculated by multiplying the number of boards by the length of one (6 m): L = 316 ∙ 6 = 1896 running meters.
Sparse crate
- We determine the number of boards for the entire area, taking into account the step of the crate. To do this, divide the area of the crate by the step and by the length of the board: N = 172.54 / 0.3 m / 6 m = 95.85 pcs.
- We translate the number of boards into cubic meters, that is, we find the volume: V = 95.85 / 75.8 = 1.26 m³.
- We calculate the amount and volume of wood for the arrangement of skates, valleys and edges. According to the initial data, there is only a ridge ridge with a length of 10 m, for which 10/6 = 1.67 pieces will be needed. in one row. In the area of the ridge, usually two rows of boards are laid on each slope, so the result is multiplied by 4 and converted into cubic meters: 1.67 ∙ 4 / 75.8 = 0.088 m³.
- We find the total volume, footage and the amount of lumber for filling a single-layer sparse crate: V = 1.26 m³ + 0.088 m³ + 10% margin ≈ 1.48 m³, L = (95.85 + 1.67 ∙ 4) ∙ 1, 1 ∙ 6 ≈ 677 running meters ≈ 113 pieces.
The metal crate for corrugated board is calculated in the same way. You can check the accuracy of manual calculations using a calculator on the website of the supplier of lumber or metal products.
How to save money on crate
At current prices, an edged board with a section of 22X100X6000 grades 1-3, according to our example, will cost about 50 thousand rubles with antiseptic treatment to stuff a solid crate and about 20 thousand rubles to create a sparse structure. As you can see, the money is a lot, so you need to know how you can save money without compromising the quality of the crate.
- Use a working section board. Experienced builders have long and successfully used this loophole, which brings significant benefits. Such boards correspond to sawing materials of the first grade, made according to GOST 8486-86, but have a 5 mm smaller cross-section. Thanks to this, the number of boards in 1 m³ is higher, and the savings are about 15-20%.
- To buy sawing out of season, when the demand for it is much lower, which is why sellers offer good discounts. In addition, wood that has matured over the winter is convenient for sorting - deformed and damaged products are clearly visible.
- Purchase rough and basic lumber in bulk during construction from scratch, which will also make it possible to significantly save money, because wholesale is always cheaper.
- If the roof design allows, then sometimes it is advisable to prepare small-sized products, since their cost is lower.
- When building a country house, purchase a quota for deforestation from the local administration, obtain permission from the forestry, independently harvest wood and bring it to the sawmill.
- And of course, you need to make a purchase from a trusted seller who values his reputation and will not allow misgrading and deception.
Sometimes, in order to save money, it is advised to purchase boards of a lower grade. Naturally, the difference in price will be considerable, but it must be borne in mind that low-grade wood will require further processing - trimming, knotting, grinding. This will entail additional costs and unnecessary hassle. So the savings in this case will turn out to be very illusory.

After sawing, the boards and bars go to the rejection line, where defects are cut out - knots, resin pockets, wane and cracks are cut
Do-it-yourself lathing for corrugated board
Consider the installation of a metal sheathing using the example of arranging a warm rigid roof. Its design is a three-layer cake, consisting of a lower and upper profile sheet and a heater between them, often mineral wool.
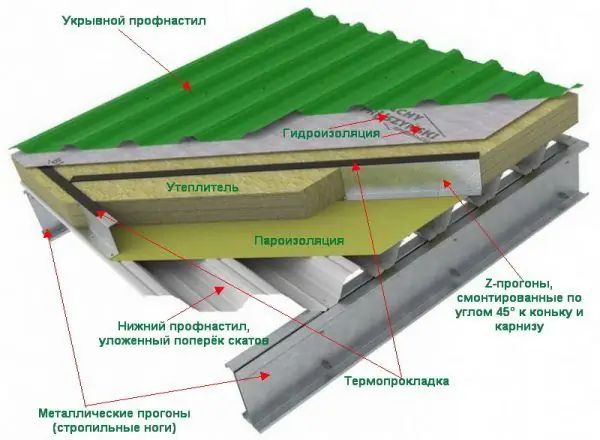
The metal structure of the warm roof is a three-layer pie with two profiled sheets on top and bottom and a heater laid between them
It should be noted that the installation of a base made of special profiled sheets with a high bearing capacity and good length - T-57, 60, 92, 135, 150 or T-160 - makes it possible to abandon the installation of the main roof girders and makes it possible to lay profiled sheets directly on the trusses or beams
-
The assembly of the insulated roof begins with laying across the slopes of the base (supporting corrugated board). The brand of profile sheets for the base is selected in accordance with the design loads on the enclosing system. The base is fixed to the beams with self-tapping screws for metal, screwing them into each wave. It is also advisable to fasten the longitudinal joints of the sheets with self-tapping screws or rivets every half a meter. This will give the base additional rigidity. It is necessary to mount the supporting profile with wide shelves to the insulation to prevent it from subsiding.

Installation of bearing corrugated board For a metal roofing structure, the base is bearing profiled sheets laid on beams or trusses with wide shelves towards the insulation
-
A vapor barrier material is laid on the base and the joints of the canvases are glued with a special tape to ensure the normal operation of the vapor barrier.

Laying the vapor barrier on the base When arranging a metal lathing, a vapor barrier is laid over the base with an overlap with the obligatory gluing of the joints of the sheets
-
Following this, intermediate Z-runs with a wall thickness of 1.0-1.5 mm are installed, which are the crate for a metal non-runner structure. Since the base is laid perpendicular to the slopes, and the covering profile for free drainage will be mounted along them, the Z-girders are arranged diagonally at an angle of 45 ° relative to the cornice. This will evenly distribute the load from the outer coating to the supporting base and prevent deformation. In the area of the ridge ridge, cornice and transverse lock of the covering material (with slopes more than 12 m), Z-girders are installed perpendicular to the slopes. The distance runs are fixed with self-tapping screws for each wave of the base.

Mounted remote runs Intermediate Z-girders in a metal, non-runner structure are crate for corrugated board - laid diagonally, they evenly distribute the load on the supporting base
-
A self-adhesive thermal pad is laid along the entire length of the purlins to eliminate cold bridges and increase the sound insulation of the metal roof. The thickness of the seal should be 5 mm, and the width should be between 50 and 70 mm.

Thermal pad sticker To eliminate cold bridges and increase the sound insulation of the metal roof, self-adhesive thermal pads are laid along the upper edge of the distance runs
-
Insulating material is laid between the Z-girders. The thickness of the insulating layer should be commensurate with the heat engineering calculations, but not more than the height of the intermediate runs.

Insulation laying In a metal structure, the insulation is laid between the Z-girders so that the heat insulator layer does not go beyond the edges of the girders
-
On top of the heat insulator, parallel to the eaves overhang, lay a superdiffusion membrane with overlaps and overlaps according to the manufacturer's instructions and mount the covering flooring, fixing it with self-tapping screws: at the points of attachment to the base in each wave, at the points of attachment to the crate - through the wave.

Installation of covering corrugated board Laying the superdiffusion membrane along the upper edges of the Z-girders ensures good ventilation of the under-roof space
-
To improve the waterproofing qualities of the corrugated board, a self-adhesive gasket is installed in the longitudinal joint of the sheets (lock) and additionally every half meter along the entire lock is fastened with self-tapping screws.

Longitudinal connection of profiled sheets To improve the sealing of joints, gaskets are inserted into the longitudinal locks and, additionally, along the entire length, they are fixed with self-tapping screws every half a meter.
For arranging a cold roof, beams welded to metal trusses will serve as lathing, with a step due to the roof structure and loads. Then corrugated board is mounted on them.
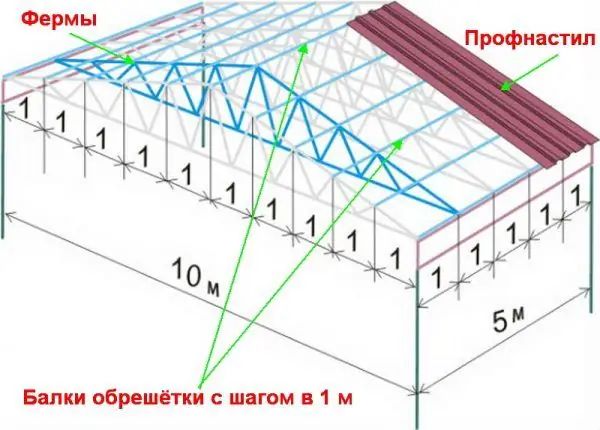
Beams welded to metal trusses serve as lathing for cold roofs
Installation of wooden lathing is simpler than metal and is reduced to the following operations.
- After all the lumber has been sorted, those that will be used for lathing and treated with an antiseptic are selected, wind boards are stuffed along the cornice and gables. They should be thicker than the main sheathing boards, since they are designed to protect the roof from strong gusty winds.
- On the upper edge of the rafters, a waterproofing material is laid, the lower edge of which is brought out to the wind cornice board, so that in the future the condensate will drain into the drip-line arranged under it.
- The waterproofing is fixed with counter-rails stuffed along the rafters. Counter-rails must be selected perfectly even in order to smooth out possible defects due to poor-quality rafter processing.
- On top of the counter-lattice, slats are stuffed with the selected pitch, using nails for fastening, the length of which is 3 times the thickness of the lathing. Only in this case the attachment points are guaranteed to withstand any loads. The lengthening is done in a checkerboard pattern with respect to the rafters, alternating the joints.
-
Covering corrugated board is mounted.

Installation of wooden lathing Wooden lathing is a structure made of boards or bars located across the rafters on top of the counter battens, on which the roofing is laid
When filling the battens, special attention should be paid to the places of passage through the roof of smoke and ventilation ducts, valleys, ridge ridge and dormer windows. In these zones, the sparse sheathing is reinforced with additional boards or bars.
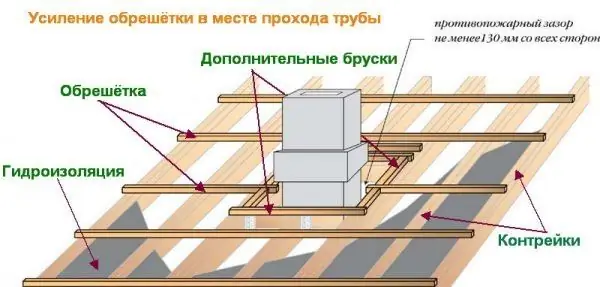
All structures located on the roof are subject to heavy snow and wind loads, therefore reinforcement of the sheathing is necessary around them
Video: installation of crate for corrugated board
Counter grating for corrugated board
Among the wide variety of roofing materials, it is important to know how to properly install one or another element of the roofing structure and what functions it performs. A lot of controversy is caused by the counter-lattice - is it needed for corrugated board. In most cases, experts give a positive answer. There are several reasons for this.
- A metal roof especially needs free air circulation. The counter-lattice, stuffed over the waterproofing, provides a sufficient ventilation passage, protecting all elements of the roof from decay and destruction. This is very important when covering the roof with profiled sheets with a low wave, under which frequent or continuous lathing is provided, which makes it difficult to ventilate the roof.
- Counter battens support the waterproofing material and prevent it from sagging. Thanks to the counter lattice, the waterproofer remains level, well-stretched and perfectly copes with its purpose.
- In some cases, with poor processing of the rafters, counter-rails stuffed along them level the load-bearing elements of the roof.
- The counter-lattice does not allow the waterproofing material to come into contact with the lathing, due to which the condensate coming out of the insulation flows freely into the drip, without causing harm to the lathing and covering material.
Thus, the counter-lattice for corrugated board performs significant functions, therefore it is necessary to mount it.

The counter-lattice is an obligatory element of the roof structure, which supports the waterproofing material and provides free air circulation in the under-roof space
The installation of the counter grill is extremely simple. After laying the waterproofing material along the rafters, pre-prepared strips are carefully packed along their upper edge. The width of the bars should be slightly less than the width of the supporting rafters, and the thickness should be from 25 to 40 mm. Bars are harvested in such a way that 3 strips with gaps between them of 150-300 mm are laid along the entire height of the slope, although it all depends on the roof design and the length of the slopes.
Video: counter grill, to do or not
In conclusion, we can say that no matter what crate is chosen, one cannot save on the quality of materials for it. Only first-class lumber and metal products that meet the standards, as well as compliance with standards, recommendations and installation rules, will guarantee a long-term and flawless service of the entire roof structure.
Recommended:
Projects Of Houses With A Garage Under One Roof, What Needs To Be Taken Into Account During Construction, And How To Properly Operate

Combining a house and a garage: design features. Options for placing a garage under the same roof as the house. Operation and maintenance rules
Lathing For Metal Tiles: What Needs To Be Considered During Installation And How To Correctly Calculate The Amount Of Material + Diagram And Video

What is better to make a crate for a metal tile. What is the lathing step. How to calculate lumber. Errors in the installation of battens and metal tiles
Lathing For Ondulin, What Needs To Be Taken Into Account During Installation And How To Correctly Calculate The Amount Of Material

How to make a crate for ondulin: the materials used and their calculation. Recommended spacing, size and thickness of structural elements. Installation of battens for ondulin
Lathing For A Profiled Sheet, What Needs To Be Taken Into Account During Installation And How To Correctly Calculate The Amount Of Material

What is the crate for corrugated board assembled from? Step, dimensions and thickness of the structure. Instructions for the manufacture of counter-battens and battens for profiled sheets
Lathing For A Soft Roof, What Needs To Be Taken Into Account During Installation And How To Correctly Calculate The Amount Of Material

Types of sheathing for a soft roof. List of materials and their calculation. Solid lathing along the sparse. Installation of battens and counter battens for soft roofs
